diff --git a/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/README.md b/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/README.md
index 50ec899..1b10c32 100644
--- a/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/README.md
+++ b/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/README.md
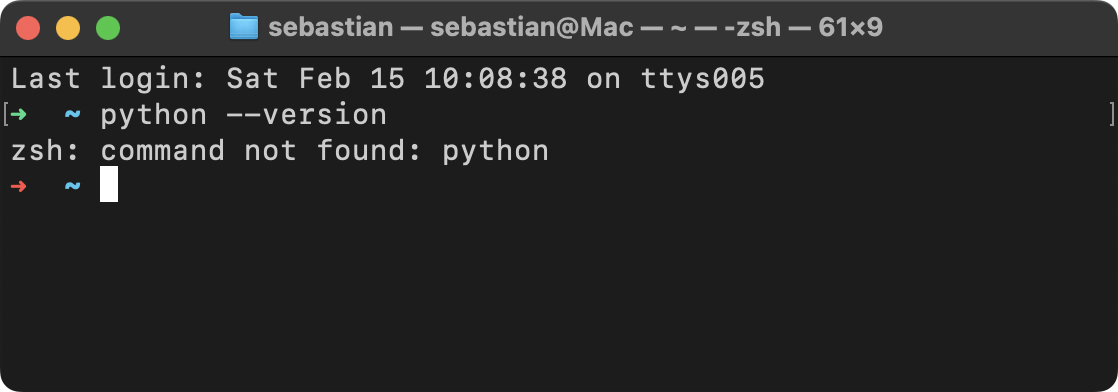
@@ -48,6 +48,7 @@ Otherwise, if Python is not installed or is an older version, you can install it
+
**Linux (Ubuntu/Debian)**
```bash
@@ -56,6 +57,7 @@ sudo apt install python3.10 python3.10-venv python3.10-dev
```
+
**macOS**
If you use Homebrew, install Python with:
@@ -72,6 +74,7 @@ I recommend installing a Python version that is at least two versions older than
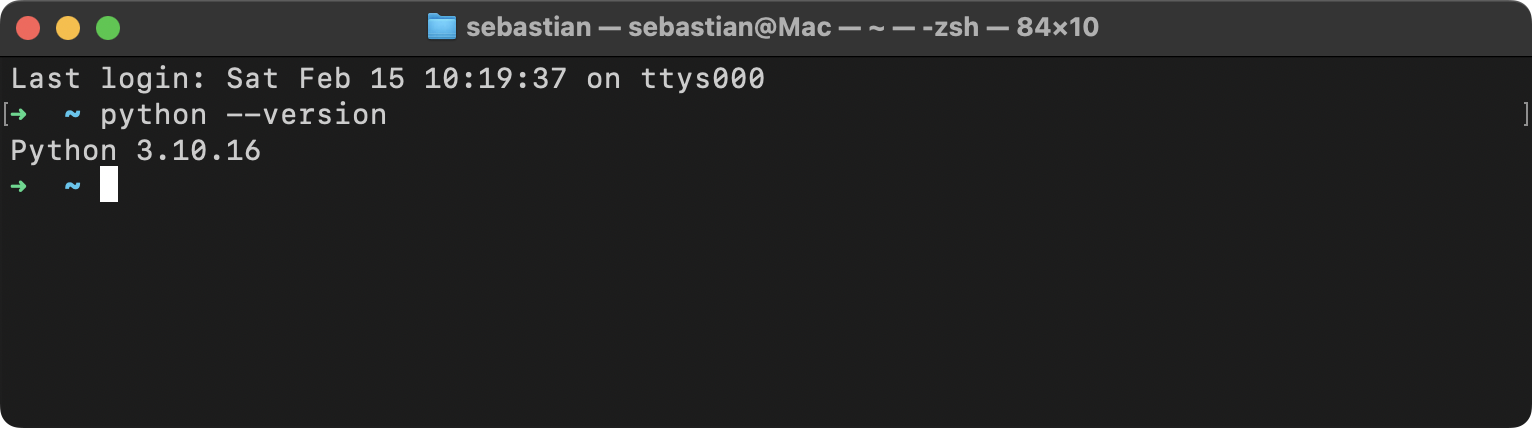
+
**Windows**
Download and run the installer from the official website: [https://www.python.org/downloads/](https://www.python.org/downloads/).
@@ -87,6 +90,7 @@ I recommend installing a Python version that is at least 2 versions older than t
I highly recommend installing Python packages in a separate virtual environment to avoid modifying system-wide packages that your OS may depend on. To create a virtual environment in the current folder, follow the three steps below.
+
**1. Install uv**
```bash
@@ -94,6 +98,7 @@ pip install uv
```
+
**2. Create the virtual environment**
```bash
@@ -101,6 +106,7 @@ uv venv --python=python3.10
```
+
**3. Activate the virtual environment**
```bash
@@ -146,6 +152,7 @@ uv pip install -U -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/r
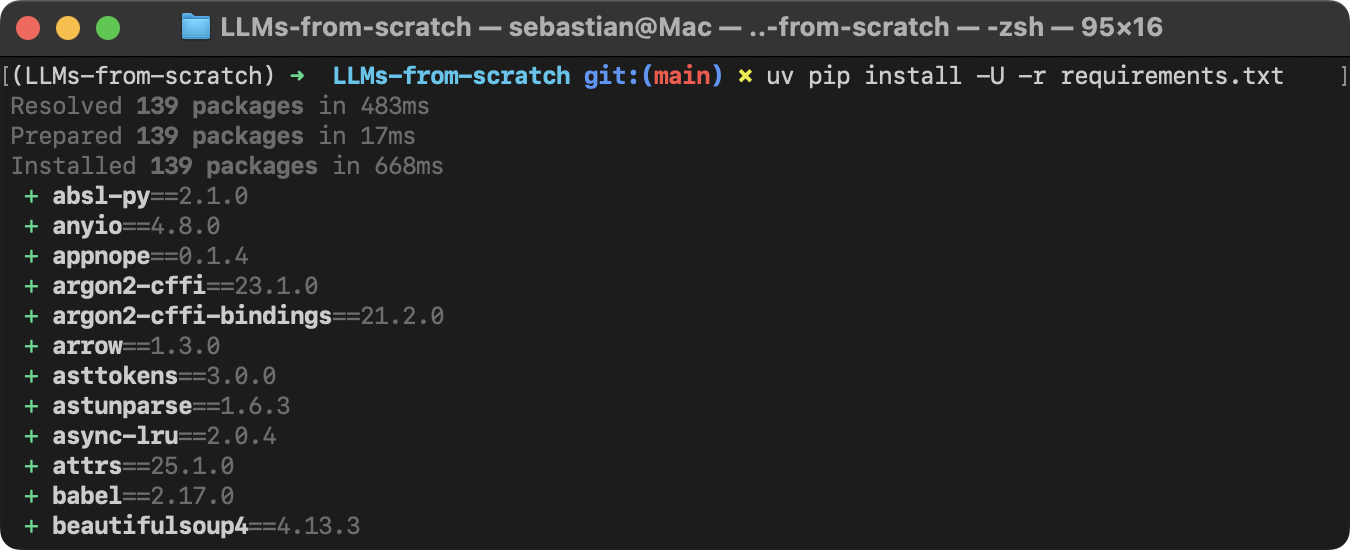
+
**Finalizing the setup**
That’s it! Your environment should now be ready for running the code in the repository.
@@ -169,6 +176,7 @@ uv pip install packagename
If problems persist, consider [opening a discussion](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions) on GitHub or working through the *Option 2: Using Conda* section below.
+
**Start working with the code**
Once everything is set up, you can start working with the code files. For instance, launch [JupyterLab](https://jupyterlab.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) by running:
diff --git a/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-uv.md b/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-uv.md
index b60d330..bce0ce6 100644
--- a/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-uv.md
+++ b/setup/01_optional-python-setup-preferences/native-uv.md
@@ -13,6 +13,7 @@ In this tutorial, I am using a computer running macOS, but this workflow is simi
Uv can be installed as follows, depending on your operating system.
+
**macOS and Linux**
```bash
@@ -26,6 +27,7 @@ wget -qO- https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
```
+
**Windows**
```bash
@@ -75,6 +77,7 @@ uv add packaging
Alternatively, you can still install the dependencies directly from the repository using `uv pip install`. Note that this requires creating and activating the virtual environment manually:
+
**1. Create a new virtual environment**
Run the following command to manually create a new virtual environment, which will be saved via a new `.venv` subfolder:
@@ -84,6 +87,7 @@ uv venv --python=python3.10
```
+
**2. Activate virtual environment**
Next, we need to activate this new virtual environment.
@@ -101,6 +105,7 @@ On Windows (PowerShell):
```
+
**3. Install dependencies**
Finally, we can install dependencies from a remote location using the `uv pip` interface:
@@ -115,6 +120,7 @@ uv pip install -U -r https://raw.githubusercontent.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/r
## 4. Run Python code
+
**Finalizing the setup**
Your environment should now be ready to run the code in the repository.
@@ -153,6 +159,7 @@ python setup/02_installing-python-libraries/python_environment_check.py
```
+
**Launching JupyterLab**
You can launch a JupyterLab instance via:


