+
+| Model | Model Download Link |
+Model Storage Size (GB) |
+Total Score |
+Description |
+
+
+| PP-DocBee-2B | Inference Model |
+4.2 |
+765 |
+PP-DocBee is a self-developed multimodal large model by the PaddlePaddle team, focusing on document understanding, and it performs excellently in Chinese document understanding tasks. The model is fine-tuned and optimized using nearly 5 million multimodal datasets for document understanding, including general VQA, OCR, charts, text-rich documents, mathematics and complex reasoning, synthetic data, and pure text data, with different training data ratios set. On several authoritative English document understanding evaluation lists in academia, PP-DocBee has basically achieved SOTA for models of the same parameter scale. In terms of internal business Chinese scenario indicators, PP-DocBee also outperforms the current popular open-source and closed-source models. |
+
+
+| PP-DocBee-7B | Inference Model |
+15.8 |
+- |
+
+
+| PP-DocBee2-3B | Inference Model |
+7.6 |
+852 |
+PP-DocBee2 is a self-developed multimodal large model by the PaddlePaddle team, further optimizing the base model on the foundation of PP-DocBee and introducing a new data optimization scheme to improve data quality. Using a small amount of 470,000 data generated by a self-developed data synthesis strategy, PP-DocBee2 performs better in Chinese document understanding tasks. In terms of internal business Chinese scenario indicators, PP-DocBee2 improves by about 11.4% compared to PP-DocBee, and also outperforms the current popular open-source and closed-source models of the same scale. |
+
+
+
+
+
+
+| Method |
+Description |
+Parameter |
+Type |
+Description |
+Default |
+
+
+
+print() |
+Print results to terminal |
+format_json |
+bool |
+Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
+True |
+
+
+indent |
+int |
+Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
+4 |
+
+
+ensure_ascii |
+bool |
+Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
+False |
+
+
+save_to_json() |
+Save the result as a json format file |
+save_path |
+str |
+Path of the file to be saved. When it is a directory, the naming of the saved file is consistent with the input file type. |
+None |
+
+
+indent |
+int |
+Specify the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
+4 |
+
+
+ensure_ascii |
+bool |
+Control whether non-ASCII characters are escaped to Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False retains the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
+False |
+
+
+
+* Additionally, it also supports obtaining prediction results through attributes, as follows:
+
+
+
+
+| Method |
+Description |
+Parameter |
+Type |
+Parameter Description |
+Default Value |
+
+
+
+print() |
+Print the result to the terminal |
+format_json |
+bool |
+Whether to format the output content using JSON indentation |
+True |
+
+
+indent |
+int |
+Specifies the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
+4 |
+
+
+ensure_ascii |
+bool |
+Controls whether to escape non-ASCII characters into Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
+False |
+
+
+save_to_json() |
+Save the result as a JSON format file |
+save_path |
+str |
+The path to save the file. When specified as a directory, the saved file is named consistent with the input file type. |
+None |
+
+
+indent |
+int |
+Specifies the indentation level to beautify the output JSON data, making it more readable, effective only when format_json is True |
+4 |
+
+
+ensure_ascii |
+bool |
+Controls whether to escape non-ASCII characters into Unicode. When set to True, all non-ASCII characters will be escaped; False will retain the original characters, effective only when format_json is True |
+False |
+
+
+
+- Calling the `print()` method will print the result to the terminal. The content printed to the terminal is explained as follows:
+
+ - `image`: `(str)` Input path of the image
+
+ - `query`: `(str)` Question regarding the input image
+
+ - `result`: `(str)` Output result of the model
+
+- Calling the `save_to_json()` method will save the above content to the specified `save_path`. If specified as a directory, the path saved will be `save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.json`, and if specified as a file, it will be saved directly to that file.
+
+* Additionally, the result can be obtained through attributes that provide the visualized images with results and the prediction results, as follows:
+
+API Reference
+
+For the main operations provided by the service:
+
+- The HTTP request method is POST.
+- Both the request body and response body are JSON data (JSON object).
+- When the request is processed successfully, the response status code is
200, and the response body has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+
+
+
+
+logId |
+string |
+UUID of the request. |
+
+
+errorCode |
+integer |
+Error code. Fixed as 0. |
+
+
+errorMsg |
+string |
+Error description. Fixed as "Success". |
+
+
+result |
+object |
+Operation result. |
+
+
+
+
+- When the request is not processed successfully, the response body has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+
+
+
+
+logId |
+string |
+UUID of the request. |
+
+
+errorCode |
+integer |
+Error code. Same as the response status code. |
+
+
+errorMsg |
+string |
+Error description. |
+
+
+
+The main operations provided by the service are as follows:
+
+Perform inference on the input message to generate a response.
+POST /document-understanding
+Note: The above interface is also known as /chat/completion, compatible with OpenAI interfaces.
+
+
+- The attributes of the request body are as follows:
+
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Required |
+Default Value |
+
+
+
+
+model |
+string |
+The name of the model to use |
+Yes |
+- |
+
+
+messages |
+array |
+List of dialogue messages |
+Yes |
+- |
+
+
+max_tokens |
+integer |
+Maximum number of tokens to generate |
+No |
+1024 |
+
+
+temperature |
+float |
+Sampling temperature |
+No |
+0.1 |
+
+
+top_p |
+float |
+Core sampling probability |
+No |
+0.95 |
+
+
+stream |
+boolean |
+Whether to output in streaming mode |
+No |
+false |
+
+
+max_image_tokens |
+int |
+Maximum number of input tokens for images |
+No |
+None |
+
+
+
+
+Each element in messages is an object with the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Required |
+
+
+
+
+role |
+string |
+Message role (user/assistant/system) |
+Yes |
+
+
+content |
+string or array |
+Message content (text or mixed media) |
+Yes |
+
+
+
+
+When content is an array, each element is an object with the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Required |
+Default Value |
+
+
+
+
+type |
+string |
+Content type (text/image_url) |
+Yes |
+- |
+
+
+text |
+string |
+Text content (when type is text) |
+Conditionally required |
+- |
+
+
+image_url |
+string or object |
+Image URL or object (when type is image_url) |
+Conditionally required |
+- |
+
+
+
+
+When image_url is an object, it has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Required |
+Default Value |
+
+
+
+
+url |
+string |
+Image URL |
+Yes |
+- |
+
+
+detail |
+string |
+Image detail processing method (low/high/auto) |
+No |
+auto |
+
+
+
+
+When the request is processed successfully, the result in the response body has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+
+
+
+
+id |
+string |
+Request ID |
+
+
+object |
+string |
+Object type (chat.completion) |
+
+
+created |
+integer |
+Creation timestamp |
+
+
+choices |
+array |
+Generated result options |
+
+
+usage |
+object |
+Token usage |
+
+
+
+
+Each element in choices is a Choice object with the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Optional Values |
+
+
+
+
+finish_reason |
+string |
+Reason for the model to stop generating tokens |
+stop (natural stop)
length (reached max token count)
tool_calls (called a tool)
content_filter (content filtering)
function_call (called a function, deprecated) |
+
+
+index |
+integer |
+Index of the option in the list |
+- |
+
+
+logprobs |
+object | null |
+Log probability information of the option |
+- |
+
+
+message |
+ChatCompletionMessage |
+Chat message generated by the model |
+- |
+
+
+
+
+The message object has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+Remarks |
+
+
+
+
+content |
+string | null |
+Message content |
+May be empty |
+
+
+refusal |
+string | null |
+Refusal message generated by the model |
+Provided when content is refused |
+
+
+role |
+string |
+Role of the message author |
+Fixed as "assistant" |
+
+
+audio |
+object | null |
+Audio output data |
+Provided when audio output is requested
Learn more |
+
+
+function_call |
+object | null |
+Name and parameters of the function to be called |
+Deprecated, recommended to use tool_calls |
+
+
+tool_calls |
+array | null |
+Tool calls generated by the model |
+Such as function calls |
+
+
+
+
+The usage object has the following attributes:
+
+
+
+| Name |
+Type |
+Meaning |
+
+
+
+
+prompt_tokens |
+integer |
+Number of prompt tokens |
+
+
+completion_tokens |
+integer |
+Number of generated tokens |
+
+
+total_tokens |
+integer |
+Total number of tokens |
+
+
+
+An example of a result is as follows:
+{
+ "id": "ed960013-eb19-43fa-b826-3c1b59657e35",
+ "choices": [
+ {
+ "finish_reason": "stop",
+ "index": 0,
+ "message": {
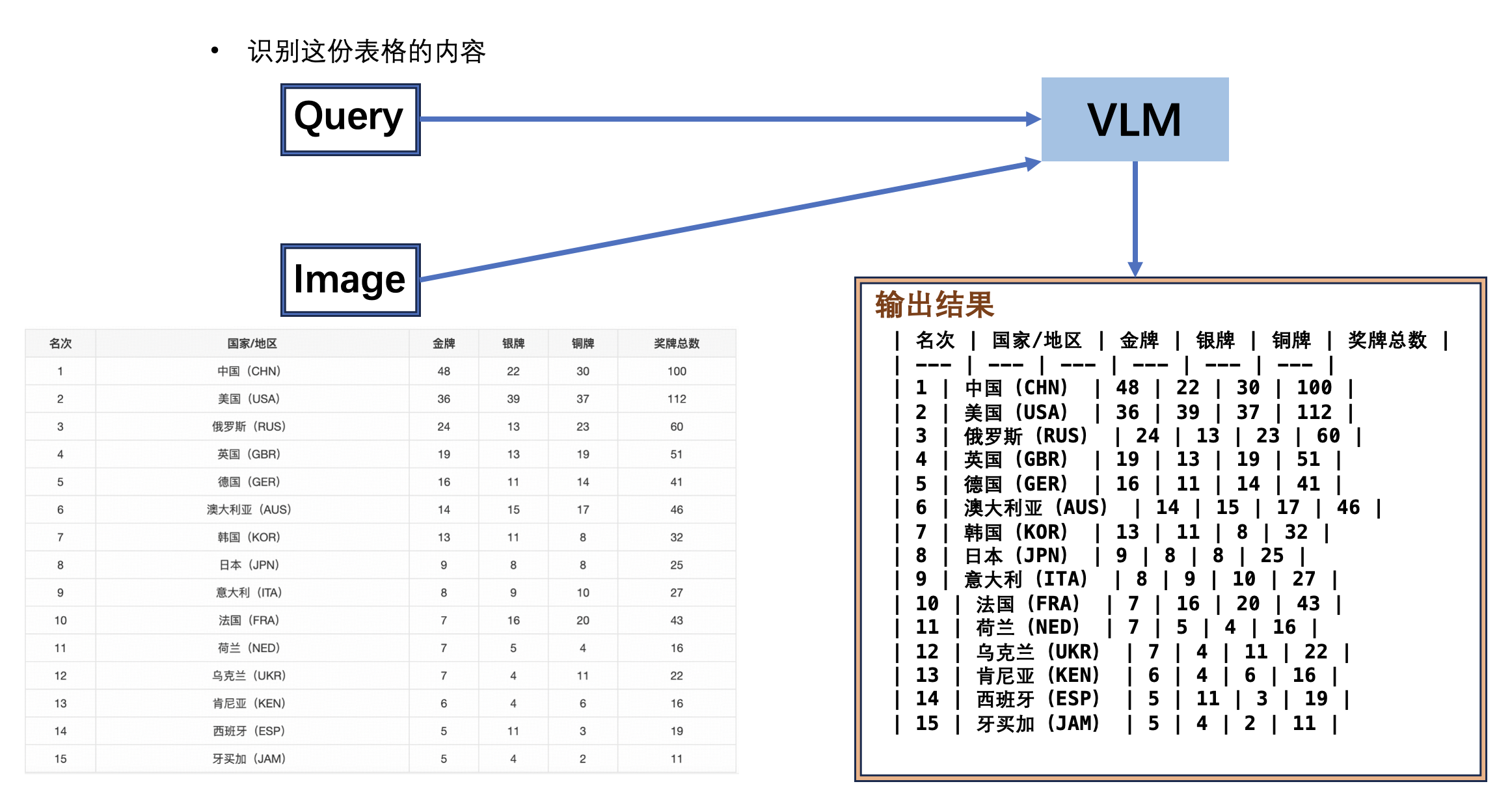
+ "content": "| 名次 | 国家/地区 | 金牌 | 银牌 | 铜牌 | 奖牌总数 |\n| --- | --- | --- | --- | --- | --- |\n| 1 | 中国(CHN) | 48 | 22 | 30 | 100 |\n| 2 | 美国(USA) | 36 | 39 | 37 | 112 |\n| 3 | 俄罗斯(RUS) | 24 | 13 | 23 | 60 |\n| 4 | 英国(GBR) | 19 | 13 | 19 | 51 |\n| 5 | 德国(GER) | 16 | 11 | 14 | 41 |\n| 6 | 澳大利亚(AUS) | 14 | 15 | 17 | 46 |\n| 7 | 韩国(KOR) | 13 | 11 | 8 | 32 |\n| 8 | 日本(JPN) | 9 | 8 | 8 | 25 |\n| 9 | 意大利(ITA) | 8 | 9 | 10 | 27 |\n| 10 | 法国(FRA) | 7 | 16 | 20 | 43 |\n| 11 | 荷兰(NED) | 7 | 5 | 4 | 16 |\n| 12 | 乌克兰(UKR) | 7 | 4 | 11 | 22 |\n| 13 | 肯尼亚(KEN) | 6 | 4 | 6 | 16 |\n| 14 | 西班牙(ESP) | 5 | 11 | 3 | 19 |\n| 15 | 牙买加(JAM) | 5 | 4 | 2 | 11 |\n",
+ "role": "assistant"
+ }
+ }
+ ],
+ "created": 1745218041,
+ "model": "pp-docbee",
+ "object": "chat.completion"
+}
+
 +
+The general document image preprocessing pipeline includes the following module. Each module can be trained and inferred independently and contains multiple models. For more details, click the corresponding module to view the documentation.
+
+- [Document-like Vision Language Model Module](../module_usage/doc_vlm.md)
+
+In this pipeline, you can choose the model to use based on the benchmark data below.
+
+
+
+The general document image preprocessing pipeline includes the following module. Each module can be trained and inferred independently and contains multiple models. For more details, click the corresponding module to view the documentation.
+
+- [Document-like Vision Language Model Module](../module_usage/doc_vlm.md)
+
+In this pipeline, you can choose the model to use based on the benchmark data below.
+
+