92 KiB
| comments |
|---|
| true |
PaddleOCR-VL 使用教程
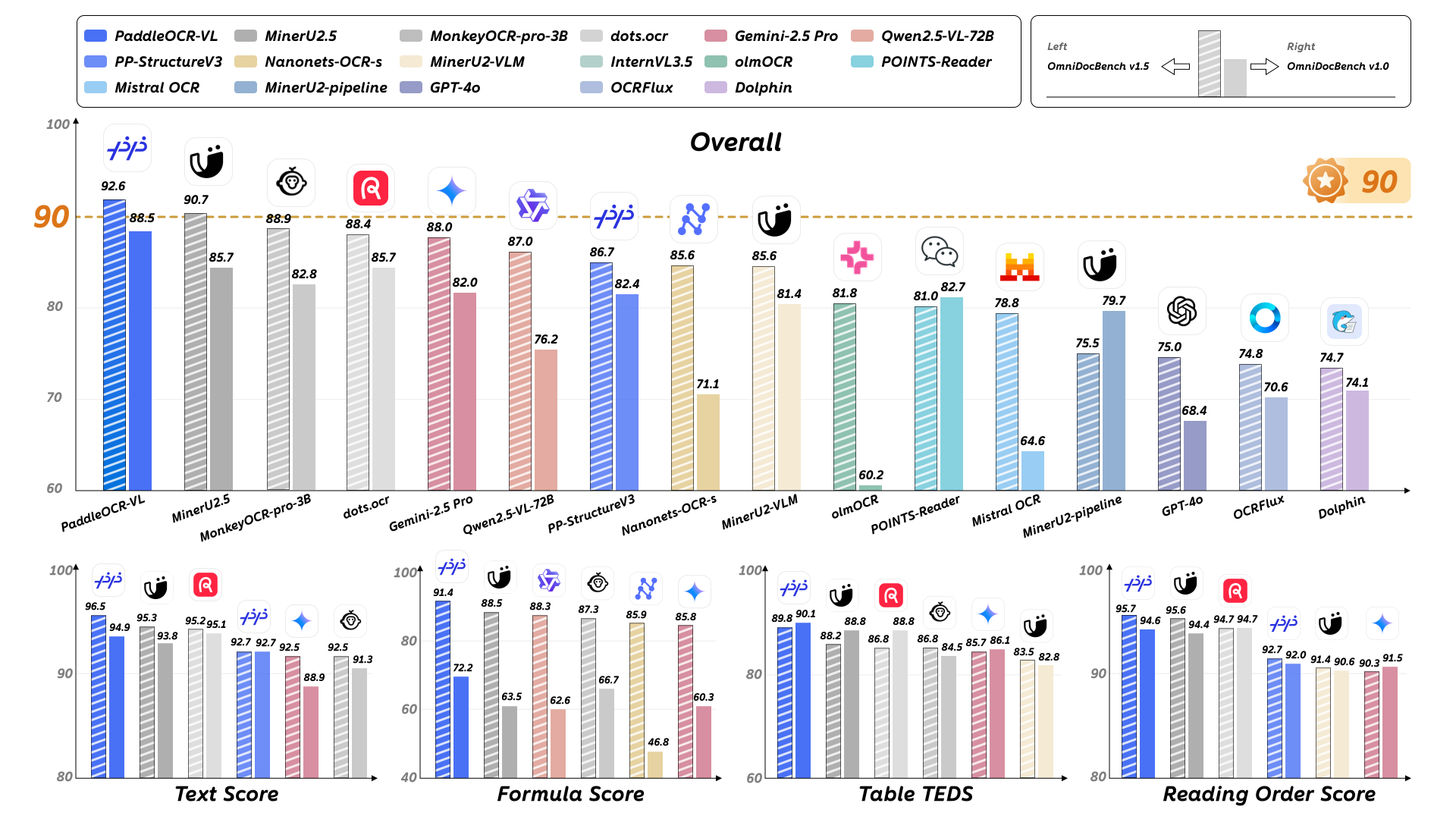
PaddleOCR-VL 是一款先进、高效的文档解析模型,专为文档中的元素识别设计。其核心组件为 PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B,这是一种紧凑而强大的视觉语言模型(VLM),它由 NaViT 风格的动态分辨率视觉编码器与 ERNIE-4.5-0.3B 语言模型组成,能够实现精准的元素识别。该模型支持 109 种语言,并在识别复杂元素(如文本、表格、公式和图表)方面表现出色,同时保持极低的资源消耗。通过在广泛使用的公开基准与内部基准上的全面评测,PaddleOCR-VL 在页级级文档解析与元素级识别均达到 SOTA 表现。它显著优于现有的基于Pipeline方案和文档解析多模态方案以及先进的通用多模态大模型,并具备更快的推理速度。这些优势使其非常适合在真实场景中落地部署。
PaddleOCR-VL 对推理设备的支持情况
目前 PaddleOCR-VL 有四种推理方式,支持的推理设备不完全相同,请确认您的推理设备是否满足下表要求再进行 PaddleOCR-VL 的推理部署:
| 推理方式 | 英伟达 GPU | 昆仑芯 XPU | 海光 DCU | 沐曦 GPU | 天数 GPU | x64 CPU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PaddlePaddle | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | ✅ |
| vLLM | ✅ | 🚧 | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
| SGLang | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
| FastDeploy | ✅ | ✅ | 🚧 | 🚧 | 🚧 | ❌ |
备注 :
- 使用英伟达 GPU 推理时需要注意 Compute Capability(简称 CC) 和 CUDA 版本(简称 CUDA)是否满足要求:
- PaddlePaddle: CC ≥ 7.0, CUDA ≥ 11.8
- vLLM: CC ≥ 8.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- SGLang: 8.0 ≤ CC < 12.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- FastDeploy: 8.0 ≤ CC < 12.0, CUDA ≥ 12.6
- CC ≥ 8 的常见显卡包括 RTX 30/40/50 系列及 A10/A100 等,更多型号可查看 CUDA GPU 计算能力
- 虽然 vLLM 可在 T4/V100 等 CC 7.x 的 NVIDIA GPU 上启动,但容易出现超时或 OOM,不推荐使用。
- 当前,PaddleOCR-VL 暂不支持 ARM 架构 CPU。后续将根据实际需求扩展更多硬件支持,敬请期待!
- vLLM、SGLang 和 FastDeploy 无法在 Windows 或 macOS 上原生运行,请使用我们提供的 Docker 镜像。
由于不同硬件所需的依赖各不相同,如果您的硬件满足上述表格的要求,请参考下表查看对应的教程进行环境配置:
| 硬件类型 | 环境配置教程 |
|---|---|
| x64 CPU | 本教程 |
| 英伟达 GPU |
|
| 昆仑芯 XPU | PaddleOCR-VL XPU 环境配置教程 |
| 海光 DCU | PaddleOCR-VL DCU 环境配置教程 |
例如您使用的是 RTX 50 系 GPU,满足 PaddlePaddle 和 vLLM 推理方式的设备要求,请参考 PaddleOCR-VL NVIDIA Blackwell 架构 GPU 环境配置教程 完成环境配置后再进行 PaddleOCR-VL 的使用。
1. 环境准备
此步骤主要介绍如何搭建 PaddleOCR-VL 的运行环境,有以下两种方式,任选一种即可:
-
方法一:使用官方 Docker 镜像。
-
方法二:手动安装 PaddlePaddle 和 PaddleOCR。
1.1 方法一:使用 Docker 镜像
我们推荐使用官方 Docker 镜像(要求 Docker 版本 >= 19.03,机器装配有 GPU 且 NVIDIA 驱动支持 CUDA 12.6 或以上版本):
docker run \
-it \
--gpus all \
--network host \
--user root \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest \
/bin/bash
# 在容器中调用 PaddleOCR CLI 或 Python API
如果您希望在无法连接互联网的环境中使用 PaddleOCR-VL,请将上述命令中的 ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest (镜像的大小约为 8 GB)更换为离线版本镜像 ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline(镜像大小约为 10 GB)。您需要在可以联网的机器上拉取镜像,将镜像导入到离线机器,然后在离线机器使用该镜像启动容器。例如:
# 在能够联网的机器上执行
docker pull ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline
# 将镜像保存到文件中
docker save ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-vl:latest-offline -o paddleocr-vl-latest-offline.tar
# 将镜像文件传输到离线机器
# 在离线机器上执行
docker load -i paddleocr-vl-latest-offline.tar
# 之后可以在离线机器上使用 `docker run` 启动容器
1.2 方法二:手动安装 PaddlePaddle 和 PaddleOCR
如果您无法使用 Docker,也可以手动安装 PaddlePaddle 和 PaddleOCR。要求 Python 版本为 3.8–3.12。
我们强烈推荐您在虚拟环境中安装 PaddleOCR-VL,以避免发生依赖冲突。 例如,使用 Python venv 标准库创建虚拟环境:
# 创建虚拟环境
python -m venv .venv_paddleocr
# 激活环境
source .venv_paddleocr/bin/activate
执行如下命令完成安装:
# 以下命令安装 CUDA 12.6 版本的 PaddlePaddle,对于其他 CUDA 版本以及 CPU 版本,请参考 https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/install/quick?docurl=/documentation/docs/zh/develop/install/pip/linux-pip.html
python -m pip install paddlepaddle-gpu==3.2.1 -i https://www.paddlepaddle.org.cn/packages/stable/cu126/
python -m pip install -U "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
# 对于 Linux 系统,执行:
python -m pip install https://paddle-whl.bj.bcebos.com/nightly/cu126/safetensors/safetensors-0.6.2.dev0-cp38-abi3-linux_x86_64.whl
# 对于Windows 系统,执行:
python -m pip install https://xly-devops.cdn.bcebos.com/safetensors-nightly/safetensors-0.6.2.dev0-cp38-abi3-win_amd64.whl
请注意安装 3.2.1 及以上版本的飞桨框架,同时安装特殊版本的 safetensors。 对于 macOS 用户,请使用 Docker 进行环境搭建。
2. 快速开始
此步骤主要介绍如何使用 PaddleOCR-VL,包括如何通过 CLI 命令行方式和 Python API 方式进行使用。
PaddleOCR-VL 支持 CLI 命令行方式和 Python API 两种使用方式,其中 CLI 命令行方式更简单,适合快速验证功能,而 Python API 方式更灵活,适合集成到现有项目中。
本节所介绍的方法主要用于快速验证,其推理速度、显存占用及稳定性表现未必能满足生产环境的要求。若需部署至生产环境,我们强烈建议使用专门的推理加速框架 ,具体方法请参考下一节。
2.1 命令行方式体验
一行命令即可快速体验 PaddleOCR-VL 效果:
paddleocr doc_parser -i https://paddle-model-ecology.bj.bcebos.com/paddlex/imgs/demo_image/paddleocr_vl_demo.png
# 通过 --use_doc_orientation_classify 指定是否使用文档方向分类模型
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_doc_orientation_classify True
# 通过 --use_doc_unwarping 指定是否使用文本图像矫正模块
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_doc_unwarping True
# 通过 --use_layout_detection 指定是否使用版面区域检测排序模块
paddleocr doc_parser -i ./paddleocr_vl_demo.png --use_layout_detection False
命令行支持更多参数设置,点击展开以查看命令行参数的详细说明
| 参数 | 参数说明 | 参数类型 | |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
待预测数据,必填。
如图像文件或者PDF文件的本地路径:/root/data/img.jpg;如URL链接,如图像文件或PDF文件的网络URL:示例;如本地目录,该目录下需包含待预测图像,如本地路径:/root/data/(当前不支持目录中包含PDF文件的预测,PDF文件需要指定到具体文件路径)。
|
str |
|
save_path |
指定推理结果文件保存的路径。如果不设置,推理结果将不会保存到本地。 | str |
|
layout_detection_model_name |
版面区域检测排序模型名称。如果不设置,将会使用默认模型。 | str |
|
layout_detection_model_dir |
版面区域检测排序模型的目录路径。如果不设置,将会下载官方模型。 | str |
|
layout_threshold |
版面模型得分阈值。0-1 之间的任意浮点数。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值。
|
float |
|
layout_nms |
版面检测是否使用后处理NMS。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值。 | bool |
|
layout_unclip_ratio |
版面区域检测模型检测框的扩张系数。
任意大于 0 浮点数。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值
|
float |
|
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
版面检测中模型输出的检测框的合并处理模式。
|
str |
|
vl_rec_model_name |
多模态识别模型名称。如果不设置,将会使用默认模型。 | str |
|
vl_rec_model_dir |
多模态识别模型目录路径。如果不设置,将会下载官方模型。 | str |
|
vl_rec_backend |
多模态识别模型使用的推理后端。 | str |
|
vl_rec_server_url |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定服务器URL。 | str |
|
vl_rec_max_concurrency |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定最大并发请求数。 | str |
|
vl_rec_api_key |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定服务的 API key。 | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
文档方向分类模型的名称。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值。 | str |
|
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
文档方向分类模型的目录路径。如果不设置,将会下载官方模型。 | str |
|
doc_unwarping_model_name |
文本图像矫正模型的名称。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值。 | str |
|
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
文本图像矫正模型的目录路径。如果不设置,将会下载官方模型。 | str |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
是否加载并使用文档方向分类模块。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool |
|
use_doc_unwarping |
是否加载并使用文本图像矫正模块。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool |
|
use_layout_detection |
是否加载并使用版面区域检测排序模块。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为True。 |
bool |
|
use_chart_recognition |
是否使用图表解析功能。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool |
|
format_block_content |
控制是否将 block_content 中的内容格式化为Markdown格式。如果不设置,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool |
|
use_queues |
用于控制是否启用内部队列。当设置为 True 时,数据加载(如将 PDF 页面渲染为图像)、版面检测模型处理以及 VLM 推理将分别在独立线程中异步执行,通过队列传递数据,从而提升效率。对于页数较多的 PDF 文档,或是包含大量图像或 PDF 文件的目录,这种方式尤其高效。 |
bool |
|
prompt_label |
VL模型的 prompt 类型设置,当且仅当 use_layout_detection=False 时生效。 |
str |
|
repetition_penalty |
VL模型采样使用的重复惩罚参数。 | float |
|
temperature |
VL模型采样使用的温度参数。 | float |
|
top_p |
VL模型采样使用的top-p参数。 | float |
|
min_pixels |
VL模型预处理图像时允许的最小像素数。 | int |
|
max_pixels |
VL模型预处理图像时允许的最大像素数。 | int |
|
device |
用于推理的设备。支持指定具体卡号:
|
str |
|
enable_hpi |
是否启用高性能推理。 | bool |
|
use_tensorrt |
是否启用 Paddle Inference 的 TensorRT 子图引擎。如果模型不支持通过 TensorRT 加速,即使设置了此标志,也不会使用加速。 对于 CUDA 11.8 版本的飞桨,兼容的 TensorRT 版本为 8.x(x>=6),建议安装 TensorRT 8.6.1.6。 |
bool |
|
precision |
计算精度,如 fp32、fp16。 | str |
|
enable_mkldnn |
是否启用 MKL-DNN 加速推理。如果 MKL-DNN 不可用或模型不支持通过 MKL-DNN 加速,即使设置了此标志,也不会使用加速。 | bool |
|
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
MKL-DNN 缓存容量。 | int |
|
cpu_threads |
在 CPU 上进行推理时使用的线程数。 | int |
|
paddlex_config |
PaddleX产线配置文件路径。 | str |
运行结果会被打印到终端上,默认配置的 PaddleOCR-VL 的运行结果如下:
👉点击展开
{'res': {'input_path': 'paddleocr_vl_demo.png', 'page_index': None, 'model_settings': {'use_doc_preprocessor': False, 'use_layout_detection': True, 'use_chart_recognition': False, 'format_block_content': False}, 'layout_det_res': {'input_path': None, 'page_index': None, 'boxes': [{'cls_id': 6, 'label': 'doc_title', 'score': 0.9636914134025574, 'coordinate': [np.float32(131.31366), np.float32(36.450516), np.float32(1384.522), np.float32(127.984665)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9281806349754333, 'coordinate': [np.float32(585.39465), np.float32(158.438), np.float32(930.2184), np.float32(182.57469)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9840355515480042, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.023666), np.float32(200.86115), np.float32(361.41583), np.float32(343.8828)]}, {'cls_id': 14, 'label': 'image', 'score': 0.9871416091918945, 'coordinate': [np.float32(775.50574), np.float32(200.66502), np.float32(1503.3807), np.float32(684.9304)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9801855087280273, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.532196), np.float32(344.90594), np.float32(361.4413), np.float32(440.8244)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9708921313285828, 'coordinate': [np.float32(28.040405), np.float32(455.87976), np.float32(341.7215), np.float32(520.7117)]}, {'cls_id': 24, 'label': 'vision_footnote', 'score': 0.9002962708473206, 'coordinate': [np.float32(809.0692), np.float32(703.70044), np.float32(1488.3016), np.float32(750.5238)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9825374484062195, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.896561), np.float32(536.54895), np.float32(361.05237), np.float32(655.8058)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9822263717651367, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.971573), np.float32(657.4949), np.float32(362.01715), np.float32(774.625)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9767460823059082, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.407074), np.float32(776.5216), np.float32(361.31067), np.float32(846.82874)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9868153929710388, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.669495), np.float32(848.2543), np.float32(361.64703), np.float32(1062.8568)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9826608300209045, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.8025055), np.float32(1063.8615), np.float32(361.46588), np.float32(1182.8524)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.982555627822876, 'coordinate': [np.float32(8.820602), np.float32(1184.4663), np.float32(361.66394), np.float32(1302.4507)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9584776759147644, 'coordinate': [np.float32(9.170288), np.float32(1304.2161), np.float32(361.48898), np.float32(1351.7483)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9782056212425232, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.1618), np.float32(200.38202), np.float32(742.7591), np.float32(295.65146)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9844875931739807, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.73303), np.float32(297.18463), np.float32(744.00024), np.float32(441.3034)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9680547714233398, 'coordinate': [np.float32(409.39468), np.float32(455.89386), np.float32(721.7174), np.float32(520.9387)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9741666913032532, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.71606), np.float32(536.8138), np.float32(742.7112), np.float32(608.00165)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9840384721755981, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.30988), np.float32(609.39636), np.float32(743.09247), np.float32(750.3231)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9845995306968689, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.13272), np.float32(751.7772), np.float32(743.058), np.float32(894.8815)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.984852135181427, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.83267), np.float32(896.0371), np.float32(743.58215), np.float32(1038.7345)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9804865717887878, 'coordinate': [np.float32(389.08478), np.float32(1039.9119), np.float32(742.7585), np.float32(1134.4897)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.986461341381073, 'coordinate': [np.float32(388.52643), np.float32(1135.8137), np.float32(743.451), np.float32(1352.0085)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9869391918182373, 'coordinate': [np.float32(769.8341), np.float32(775.66235), np.float32(1124.9813), np.float32(1063.207)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9822869896888733, 'coordinate': [np.float32(770.30383), np.float32(1063.938), np.float32(1124.8295), np.float32(1184.2192)]}, {'cls_id': 17, 'label': 'paragraph_title', 'score': 0.9689218997955322, 'coordinate': [np.float32(791.3042), np.float32(1199.3169), np.float32(1104.4521), np.float32(1264.6985)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9713128209114075, 'coordinate': [np.float32(770.4253), np.float32(1279.6072), np.float32(1124.6917), np.float32(1351.8672)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9236552119255066, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1153.9058), np.float32(775.5814), np.float32(1334.0654), np.float32(798.1581)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9857938885688782, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.5197), np.float32(799.28015), np.float32(1506.3619), np.float32(991.1156)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9820687174797058, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.5686), np.float32(991.91095), np.float32(1506.6023), np.float32(1110.8875)]}, {'cls_id': 22, 'label': 'text', 'score': 0.9866049885749817, 'coordinate': [np.float32(1151.6919), np.float32(1112.1301), np.float32(1507.1611), np.float32(1351.9504)]}]}}}
运行结果参数说明可以参考2.2 Python脚本方式集成中的结果解释。
注:由于 PaddleOCR-VL 的默认模型较大,推理速度可能较慢,建议实际推理使用3. 使用推理加速框架提升 VLM 推理性能 方式进行快速推理。
2.2 Python脚本方式集成
命令行方式是为了快速体验查看效果,一般来说,在项目中,往往需要通过代码集成,您可以通过几行代码即可完成 PaddleOCR-VL 的快速推理,推理代码如下:
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_doc_orientation_classify=True) # 通过 use_doc_orientation_classify 指定是否使用文档方向分类模型
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_doc_unwarping=True) # 通过 use_doc_unwarping 指定是否使用文本图像矫正模块
# pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(use_layout_detection=False) # 通过 use_layout_detection 指定是否使用版面区域检测排序模块
output = pipeline.predict("./paddleocr_vl_demo.png")
for res in output:
res.print() ## 打印预测的结构化输出
res.save_to_json(save_path="output") ## 保存当前图像的结构化json结果
res.save_to_markdown(save_path="output") ## 保存当前图像的markdown格式的结果
如果是 PDF 文件,会将 PDF 的每一页单独处理,每一页的 Markdown 文件也会对应单独的结果。如果希望整个 PDF 文件转换为 Markdown 文件,建议使用以下的方式运行:
from pathlib import Path
from paddleocr import PaddleOCRVL
input_file = "./your_pdf_file.pdf"
output_path = Path("./output")
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL()
output = pipeline.predict(input=input_file)
markdown_list = []
markdown_images = []
for res in output:
md_info = res.markdown
markdown_list.append(md_info)
markdown_images.append(md_info.get("markdown_images", {}))
markdown_texts = pipeline.concatenate_markdown_pages(markdown_list)
mkd_file_path = output_path / f"{Path(input_file).stem}.md"
mkd_file_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
with open(mkd_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.write(markdown_texts)
for item in markdown_images:
if item:
for path, image in item.items():
file_path = output_path / path
file_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
image.save(file_path)
注:
- 在示例代码中,
use_doc_orientation_classify、use_doc_unwarping参数默认均设置为False,分别表示关闭文档方向分类、文本图像矫正功能,如果需要使用这些功能,可以手动设置为True。
在上述 Python 脚本中,执行了如下几个步骤:
(1)实例化对象,具体参数说明如下:
| 参数 | 参数说明 | 参数类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
layout_detection_model_name |
版面区域检测排序模型名称。如果设置为None,将会使用默认模型。 |
str|None |
None |
layout_detection_model_dir |
版面区域检测排序模型的目录路径。如果设置为None,将会下载官方模型。 |
str|None |
None |
layout_threshold |
版面模型得分阈值。
|
float|dict|None |
None |
layout_nms |
版面检测是否使用后处理NMS。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值。 |
bool|None |
None |
layout_unclip_ratio |
版面区域检测模型检测框的扩张系数。
|
float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
版面区域检测的重叠框过滤方式。
|
str|dict|None |
None |
vl_rec_model_name |
多模态识别模型名称。如果设置为None,将会使用默认模型。 |
str|None |
None |
vl_rec_model_dir |
多模态识别模型目录路径。如果设置为None,将会下载官方模型。 |
str|None |
None |
vl_rec_backend |
多模态识别模型使用的推理后端。 | int|None |
None |
vl_rec_server_url |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定服务器URL。 | str|None |
None |
vl_rec_max_concurrency |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定最大并发请求数。 | str|None |
None |
vl_rec_api_key |
如果多模态识别模型使用推理服务,该参数用于指定服务的 API key。 | str|None |
None |
doc_orientation_classify_model_name |
文档方向分类模型的名称。如果设置为None,将会使用默认模型。 |
str|None |
None |
doc_orientation_classify_model_dir |
文档方向分类模型的目录路径。如果设置为None,将会下载官方模型。 |
str|None |
None |
doc_unwarping_model_name |
文本图像矫正模型的名称。如果设置为None,将会使用默认模型。 |
str|None |
None |
doc_unwarping_model_dir |
文本图像矫正模型的目录路径。如果设置为None,将会下载官方模型。 |
str|None |
None |
use_doc_orientation_classify |
是否加载并使用文档方向分类模块。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
是否加载并使用文本图像矫正模块。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_layout_detection |
是否加载并使用版面区域检测排序模块。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为True。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_chart_recognition |
是否加载并使用图表解析模块。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool|None |
None |
format_block_content |
控制是否将 block_content 中的内容格式化为Markdown格式。如果设置为None,将使用初始化的默认值,默认初始化为False。 |
bool|None |
None |
device |
用于推理的设备。支持指定具体卡号:
|
str|None |
None |
enable_hpi |
是否启用高性能推理。 | bool |
False |
use_tensorrt |
是否启用 Paddle Inference 的 TensorRT 子图引擎。如果模型不支持通过 TensorRT 加速,即使设置了此标志,也不会使用加速。 对于 CUDA 11.8 版本的飞桨,兼容的 TensorRT 版本为 8.x(x>=6),建议安装 TensorRT 8.6.1.6。 |
bool |
False |
precision |
计算精度,如 fp32、fp16。 | str |
"fp32" |
enable_mkldnn |
是否启用 MKL-DNN 加速推理。如果 MKL-DNN 不可用或模型不支持通过 MKL-DNN 加速,即使设置了此标志,也不会使用加速。 | bool |
True |
mkldnn_cache_capacity |
MKL-DNN 缓存容量。 | int |
10 |
cpu_threads |
在 CPU 上进行推理时使用的线程数。 | int |
8 |
paddlex_config |
PaddleX产线配置文件路径。 | str|None |
None |
(2)调用 PaddleOCR-VL 对象的 predict() 方法进行推理预测,该方法会返回一个结果列表。另外,PaddleOCR-VL 还提供了 predict_iter() 方法。两者在参数接受和结果返回方面是完全一致的,区别在于 predict_iter() 返回的是一个 generator,能够逐步处理和获取预测结果,适合处理大型数据集或希望节省内存的场景。可以根据实际需求选择使用这两种方法中的任意一种。以下是 predict() 方法的参数及其说明:
| 参数 | 参数说明 | 参数类型 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
input |
待预测数据,支持多种输入类型,必填。
|
Python Var|str|list |
|
use_doc_orientation_classify |
是否在推理时使用文档方向分类模块。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_doc_unwarping |
是否在推理时使用文本图像矫正模块。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_layout_detection |
是否在推理时使用版面区域检测排序模块。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
use_chart_recognition |
是否在推理时使用图表解析模块。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
layout_threshold |
参数含义与实例化参数基本相同。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
float|dict|None |
None |
layout_nms |
参数含义与实例化参数基本相同。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
layout_unclip_ratio |
参数含义与实例化参数基本相同。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
float|Tuple[float,float]|dict|None |
None |
layout_merge_bboxes_mode |
参数含义与实例化参数基本相同。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
str|dict|None |
None |
use_queues |
用于控制是否启用内部队列。当设置为 True 时,数据加载(如将 PDF 页面渲染为图像)、版面检测模型处理以及 VLM 推理将分别在独立线程中异步执行,通过队列传递数据,从而提升效率。对于页数较多的 PDF 文档,或是包含大量图像或 PDF 文件的目录,这种方式尤其高效。 |
bool|None |
None |
prompt_label |
VL模型的 prompt 类型设置,当且仅当 use_layout_detection=False 时生效。可填写参数为 ocr、formula、table 和 chart。 |
str|None |
None |
format_block_content |
参数含义与实例化参数基本相同。设置为None表示使用实例化参数,否则该参数优先级更高。 |
bool|None |
None |
repetition_penalty |
VL模型采样使用的重复惩罚参数。 | float|None |
None |
temperature |
VL模型采样使用的温度参数。 | float|None |
None |
top_p |
VL模型采样使用的top-p参数。 | float|None |
None |
min_pixels |
VL模型预处理图像时允许的最小像素数。 | int|None |
None |
max_pixels |
VL模型预处理图像时允许的最大像素数。 | int|None |
None |
(3)对预测结果进行处理:每个样本的预测结果均为对应的Result对象,且支持打印、保存为图片、保存为json文件的操作:
| 方法 | 方法说明 | 参数 | 参数类型 | 参数说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
print() |
打印结果到终端 | format_json |
bool |
是否对输出内容进行使用 JSON 缩进格式化。 |
True |
indent |
int |
指定缩进级别,以美化输出的 JSON 数据,使其更具可读性,仅当 format_json 为 True 时有效。 |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
控制是否将非 ASCII 字符转义为 Unicode。设置为 True 时,所有非 ASCII 字符将被转义;False 则保留原始字符,仅当format_json为True时有效。 |
False |
||
save_to_json() |
将结果保存为json格式的文件 | save_path |
str |
保存的文件路径,当为目录时,保存文件命名与输入文件类型命名一致。 | 无 |
indent |
int |
指定缩进级别,以美化输出的 JSON 数据,使其更具可读性,仅当 format_json 为 True 时有效。 |
4 | ||
ensure_ascii |
bool |
控制是否将非 ASCII 字符转义为 Unicode。设置为 True 时,所有非 ASCII 字符将被转义;False 则保留原始字符,仅当format_json为True时有效。 |
False |
||
save_to_img() |
将中间各个模块的可视化图像保存在png格式的图像 | save_path |
str |
保存的文件路径,支持目录或文件路径。 | 无 |
save_to_markdown() |
将图像或者PDF文件中的每一页分别保存为markdown格式的文件 | save_path |
str |
保存的文件路径,当为目录时,保存文件命名与输入文件类型命名一致 | 无 |
pretty |
bool |
是否美化 markdown 输出结果,将图表等进行居中操作,使 markdown 渲染后更美观。 |
True | ||
show_formula_number |
bool |
控制是否在 markdown 中将保留公式编号。设置为 True 时,保留全部公式编号;False 则仅保留公式 |
False |
||
save_to_html() |
将文件中的表格保存为html格式的文件 | save_path |
str |
保存的文件路径,支持目录或文件路径。 | 无 |
save_to_xlsx() |
将文件中的表格保存为xlsx格式的文件 | save_path |
str |
保存的文件路径,支持目录或文件路径。 | 无 |
-
调用
print()方法会将结果打印到终端,打印到终端的内容解释如下:-
input_path:(str)待预测图像或者PDF的输入路径 -
page_index:(Union[int, None])如果输入是PDF文件,则表示当前是PDF的第几页,否则为None -
model_settings:(Dict[str, bool])配置 PaddleOCR-VL 所需的模型参数use_doc_preprocessor:(bool)控制是否启用文档预处理子产线use_layout_detection:(bool)控制是否启用版面检测模块use_chart_recognition:(bool)控制是否开启图表识别功能format_block_content:(bool)控制是否在JSON中保存格式化后的markdown内容
-
doc_preprocessor_res:(Dict[str, Union[List[float], str]])文档预处理结果dict,仅当use_doc_preprocessor=True时存在input_path:(str)文档预处理子接受的图像路径,当输入为numpy.ndarray时,保存为None,此处为Nonepage_index:None,此处的输入为numpy.ndarray,所以值为Nonemodel_settings:(Dict[str, bool])文档预处理子的模型配置参数use_doc_orientation_classify:(bool)控制是否启用文档图像方向分类子模块use_doc_unwarping:(bool)控制是否启用文本图像扭曲矫正子模块
angle:(int)文档图像方向分类子模块的预测结果,启用时返回实际角度值
-
parsing_res_list:(List[Dict])解析结果的列表,每个元素为一个字典,列表顺序为解析后的阅读顺序。block_bbox:(np.ndarray)版面区域的边界框。block_label:(str)版面区域的标签,例如text,table等。block_content:(str)内容为版面区域内的内容。block_id:(int)版面区域的索引,用于显示版面排序结果。block_order(int)版面区域的顺序,用于显示版面阅读顺序,对于非排序部分,默认值为None。
-
-
调用
save_to_json()方法会将上述内容保存到指定的save_path中,如果指定为目录,则保存的路径为save_path/{your_img_basename}_res.json,如果指定为文件,则直接保存到该文件中。由于 json 文件不支持保存numpy数组,因此会将其中的numpy.array类型转换为列表形式。json中的字段内容如下:-
input_path:(str)待预测图像或者PDF的输入路径 -
page_index:(Union[int, None])如果输入是PDF文件,则表示当前是PDF的第几页,否则为None -
model_settings:(Dict[str, bool])配置 PaddleOCR-VL 所需的模型参数use_doc_preprocessor:(bool)控制是否启用文档预处理子产线use_layout_detection:(bool)控制是否启用版面检测模块use_chart_recognition:(bool)控制是否开启图表识别功能format_block_content:(bool)控制是否在JSON中保存格式化后的markdown内容
-
doc_preprocessor_res:(Dict[str, Union[List[float], str]])文档预处理结果dict,仅当use_doc_preprocessor=True时存在input_path:(str)文档预处理子接受的图像路径,当输入为numpy.ndarray时,保存为None,此处为Nonepage_index:None,此处的输入为numpy.ndarray,所以值为Nonemodel_settings:(Dict[str, bool])文档预处理子的模型配置参数use_doc_orientation_classify:(bool)控制是否启用文档图像方向分类子模块use_doc_unwarping:(bool)控制是否启用文本图像扭曲矫正子模块
angle:(int)文档图像方向分类子模块的预测结果,启用时返回实际角度值
-
parsing_res_list:(List[Dict])解析结果的列表,每个元素为一个字典,列表顺序为解析后的阅读顺序。block_bbox:(np.ndarray)版面区域的边界框。block_label:(str)版面区域的标签,例如text,table等。block_content:(str)内容为版面区域内的内容。block_id:(int)版面区域的索引,用于显示版面排序结果。block_order(int)版面区域的顺序,用于显示版面阅读顺序,对于非排序部分,默认值为None。
-
-
调用
save_to_img()方法会将可视化结果保存到指定的save_path中,如果指定为目录,则会将版面区域检测可视化图像、全局OCR可视化图像、版面阅读顺序可视化图像等内容保存,如果指定为文件,则直接保存到该文件中。 -
调用
save_to_markdown()方法会将转化后的 Markdown 文件保存到指定的save_path中,保存的文件路径为save_path/{your_img_basename}.md,如果输入是 PDF 文件,建议直接指定目录,否责多个 markdown 文件会被覆盖。
此外,也支持通过属性获取带结果的可视化图像和预测结果,具体如下:
| 属性 | 属性说明 |
|---|---|
json |
获取预测的 json 格式的结果 |
img |
获取格式为 dict 的可视化图像 |
markdown |
获取格式为 dict 的 markdown 结果 |
json属性获取的预测结果为dict类型的数据,相关内容与调用save_to_json()方法保存的内容一致。img属性返回的预测结果是一个dict类型的数据。其中,键分别为layout_det_res和layout_order_res,对应的值是Image.Image对象:分别用于显示版面区域检测和版面阅读顺序结果的可视化图像。如果没有使用可选模块,则dict中只包含layout_det_res。markdown属性返回的预测结果是一个dict类型的数据。其中,键分别为markdown_texts和markdown_images,对应的值分别是 markdown 文本,在 Markdown 中显示的图像(Image.Image对象)。
3. 使用推理加速框架提升 VLM 推理性能
默认配置下的推理性能未经过充分优化,可能无法满足实际生产需求。此步骤主要介绍如何使用 vLLM、SGLang 和 FastDeploy 推理加速框架来提升 PaddleOCR-VL 的推理性能。
3.1 启动 VLM 推理服务
启动 VLM 推理服务有以下两种方式,任选一种即可:
-
方法一:使用官方 Docker 镜像启动服务。
-
方法二:通过 PaddleOCR CLI 手动安装依赖后启动服务。
3.1.1 方法一:使用 Docker 镜像
PaddleOCR 提供了 Docker 镜像,用于快速启动 vLLM 或 FastDeploy 推理服务。可使用以下命令启动服务(要求 Docker 版本 >= 19.03,机器装配有 GPU 且 NVIDIA 驱动支持 CUDA 12.6 或以上版本):
=== "启动 vLLM 服务"
```shell
docker run \
-it \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8118 --backend vllm
```
如果您希望在无法连接互联网的环境中启动服务,请将上述命令中的 `ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest`(镜像大小约为 13 GB)更换为离线版本镜像 `ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-vllm-server:latest-offline`(镜像大小约为 15 GB)。
=== "启动 FastDeploy 服务"
```shell
docker run \
-it \
--rm \
--gpus all \
--network host \
ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest \
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --host 0.0.0.0 --port 8118 --backend fastdeploy
```
如果您希望在无法连接互联网的环境中启动服务,请将上述命令中的 `ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest`(镜像大小约为 43 GB)更换为离线版本镜像 `ccr-2vdh3abv-pub.cnc.bj.baidubce.com/paddlepaddle/paddleocr-genai-fastdeploy-server:latest-offline`(镜像大小约为 45 GB)。
启动 vLLM 或 FastDeploy 推理服务可以传入更多参数,支持的参数详见下一小节。
3.1.2 方法二:通过 PaddleOCR CLI 安装和使用
由于推理加速框架可能与飞桨框架存在依赖冲突,建议在虚拟环境中安装。以 vLLM 为例:
# 如果当前存在已激活的虚拟环境,先通过 `deactivate` 取消激活
# 创建虚拟环境
python -m venv .venv_vlm
# 激活环境
source .venv_vlm/bin/activate
# 安装 PaddleOCR
python -m pip install "paddleocr[doc-parser]"
# 安装推理加速服务依赖
paddleocr install_genai_server_deps vllm
paddleocr install_genai_server_deps 命令用法:
paddleocr install_genai_server_deps <推理加速框架名称>
当前支持的框架名称为 vllm、sglang 和 fastdeploy,分别对应 vLLM、SGLang 和 FastDeploy。
通过 paddleocr install_genai_server_deps 安装的 vLLM 与 SGLang 均为 CUDA 12.6 版本,请确保本地 NVIDIA 驱动与此版本一致或更高。
paddleocr install_genai_server_deps命令在执行过程中可能需要使用 nvcc 等 CUDA 编译工具。如果您的环境中没有这些工具(例如在使用paddleocr-vl镜像),可以从 此仓库 获取 FlashAttention 的预编译版本,先安装预编译包,再执行后续命令。例如,您在paddleocr-vl镜像中,执行python -m pip install https://github.com/mjun0812/flash-attention-prebuild-wheels/releases/download/v0.3.14/flash_attn-2.8.2+cu128torch2.8-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whl。
安装完成后,可通过 paddleocr genai_server 命令启动服务:
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --backend vllm --port 8118
该命令支持的参数如下:
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
--model_name |
模型名称 |
--model_dir |
模型目录 |
--host |
服务器主机名 |
--port |
服务器端口号 |
--backend |
后端名称,即使用的推理加速框架名称,可选 vllm 或 sglang |
--backend_config |
可指定 YAML 文件,包含后端配置 |
3.2 客户端使用方法
启动 VLM 推理服务后,客户端即可通过 PaddleOCR 调用该服务。请注意,由于客户端需要调用版面检测的顺序模型,仍建议在 GPU 等加速设备上运行客户端,以获得更稳定和高效的性能。
3.2.1 CLI 调用
可通过 --vl_rec_backend 指定后端类型(vllm-server 或 sglang-server),通过 --vl_rec_server_url 指定服务地址,例如:
paddleocr doc_parser --input paddleocr_vl_demo.png --vl_rec_backend vllm-server --vl_rec_server_url http://127.0.0.1:8118/v1
3.2.2 Python API 调用
创建 PaddleOCRVL 对象时传入 vl_rec_backend 和 vl_rec_server_url 参数:
pipeline = PaddleOCRVL(vl_rec_backend="vllm-server", vl_rec_server_url="http://127.0.0.1:8118/v1")
3.3 性能调优
默认配置是在单张 NVIDIA A100 上进行调优的,并假设客户端独占服务,因此可能不适用于其他环境。如果用户在实际使用中遇到性能问题,可以尝试以下优化方法。
3.3.1 服务端参数调整
不同推理加速框架支持的参数不同,可参考各自官方文档了解可用参数及其调整时机:
PaddleOCR VLM 推理服务支持通过配置文件进行调参。以下示例展示如何调整 vLLM 服务器的 gpu-memory-utilization 和 max-num-seqs 参数:
-
创建 YAML 文件
vllm_config.yaml,内容如下:gpu-memory-utilization: 0.3 max-num-seqs: 128 -
启动服务时指定配置文件路径,例如使用
paddleocr genai_server命令:paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --backend vllm --backend_config vllm_config.yaml
如果使用支持进程替换(process substitution)的 shell(如 Bash),也可以无需创建配置文件,直接在启动服务时传入配置项:
paddleocr genai_server --model_name PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B --backend vllm --backend_config <(echo -e 'gpu-memory-utilization: 0.3\nmax-num-seqs: 128')
3.3.2 客户端参数调整
PaddleOCR 会将来自单张或多张输入图像中的子图分组并对服务器发起并发请求,因此并发请求数对性能影响显著。
- 对 CLI 和 Python API,可通过
vl_rec_max_concurrency参数调整最大并发请求数; - 对服务化部署,可修改配置文件中
VLRecognition.genai_config.max_concurrency字段。
当客户端与 VLM 推理服务为 1 对 1 且服务端资源充足时,可适当增加并发数以提升性能;若服务端需支持多个客户端或计算资源有限,则应降低并发数,以避免资源过载导致服务异常。
3.3.3 常用硬件性能调优建议
以下配置均针对客户端与 VLM 推理服务为 1 对 1 的场景。
NVIDIA RTX 3060
- 服务端
- vLLM:
gpu-memory-utilization: 0.8 - FastDeploy:
gpu-memory-utilization: 0.8max-concurrency: 2048
- vLLM:
4. 服务化部署
此步骤主要介绍如何将 PaddleOCR-VL 部署为服务并调用,有以下两种方式,任选一种即可:
-
方法一:使用 Docker Compose 部署(推荐使用)。
-
方法二:手动安装依赖部署。
请注意,本节所介绍 PaddleOCR-VL 服务与上一节中的 VLM 推理服务有所区别:后者仅负责完整流程中的一个环节(即 VLM 推理),并作为前者的底层服务被调用。
4.1 方法一:使用 Docker Compose 部署(推荐使用)
您可以分别从 此处 和 此处 获取 Compose 文件与环境变量配置文件并下载到本地,然后在刚刚下载的文件所在目录下执行以下命令启动服务器,默认监听 8080 端口:
# 必须在 compose.yaml 和 .env 文件所在的目录中执行
docker compose up
启动后将看到类似如下输出:
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Started server process [1]
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Waiting for application startup.
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Application startup complete.
paddleocr-vl-api | INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
此方式基于 vLLM 等框架对 VLM 推理进行加速,更适合生产环境部署,但要求机器配备 GPU,并且 NVIDIA 驱动程序支持 CUDA 12.6 或以上版本。
.env 文件可用于配置环境变量,详细介绍如下:
API_IMAGE_TAG_SUFFIX:启动产线服务使用的镜像的标签后缀。默认为latest-offline,表示使用离线 GPU 镜像。VLM_BACKEND:VLM 推理后端,目前支持vllm和fastdeploy。默认为vllm。VLM_IMAGE_TAG_SUFFIX:启动 VLM 推理服务使用的镜像的标签后缀。默认为latest-offline,表示使用离线 GPU 镜像。
此外,使用此方式启动服务器后,除拉取镜像外,无需连接互联网。如需在离线环境中部署,可先在联网机器上拉取 Compose 文件中涉及的镜像,导出并传输至离线机器中导入,即可在离线环境下启动服务。
如需调整产线相关配置(如模型路径、批处理大小、部署设备等),可参考 4.4 小节。
4.2 方法二:手动安装依赖部署
执行以下命令,通过 PaddleX CLI 安装服务化部署插件:
paddlex --install serving
然后,使用 PaddleX CLI 启动服务器:
paddlex --serve --pipeline PaddleOCR-VL
启动后将看到类似如下输出,服务器默认监听 8080 端口:
INFO: Started server process [63108]
INFO: Waiting for application startup.
INFO: Application startup complete.
INFO: Uvicorn running on http://0.0.0.0:8080 (Press CTRL+C to quit)
与服务化部署相关的命令行参数如下:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
--pipeline |
PaddleX 产线注册名或产线配置文件路径。 |
--device |
产线部署设备。默认情况下,若 GPU 可用则使用 GPU,否则使用 CPU。 |
--host |
服务器绑定的主机名或 IP 地址,默认为 0.0.0.0。 |
--port |
服务器监听的端口号,默认为 8080。 |
--use_hpip |
启用高性能推理模式。请参考高性能推理文档了解更多信息。 |
--hpi_config |
高性能推理配置。请参考高性能推理文档了解更多信息。 |
如需调整产线相关配置(如模型路径、批处理大小、部署设备等),可参考 4.4 小节。
4.3 客户端调用方式
以下是服务化部署的 API 参考与多语言服务调用示例:
API 参考
对于服务提供的主要操作:
- HTTP请求方法为POST。
- 请求体和响应体均为JSON数据(JSON对象)。
- 当请求处理成功时,响应状态码为
200,响应体的属性如下:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
请求的UUID。 |
errorCode |
integer |
错误码。固定为0。 |
errorMsg |
string |
错误说明。固定为"Success"。 |
result |
object |
操作结果。 |
- 当请求处理未成功时,响应体的属性如下:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
logId |
string |
请求的UUID。 |
errorCode |
integer |
错误码。与响应状态码相同。 |
errorMsg |
string |
错误说明。 |
服务提供的主要操作如下:
infer
进行版面解析。
POST /layout-parsing
- 请求体的属性如下:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 | 是否必填 |
|---|---|---|---|
file |
string |
服务器可访问的图像文件或PDF文件的URL,或上述类型文件内容的Base64编码结果。默认对于超过10页的PDF文件,只有前10页的内容会被处理。 要解除页数限制,请在产线配置文件中添加以下配置: |
是 |
fileType |
integer|null |
文件类型。0表示PDF文件,1表示图像文件。若请求体无此属性,则将根据URL推断文件类型。 |
否 |
useDocOrientationClassify |
boolean | null |
请参阅产线对象中 predict 方法的 use_doc_orientation_classify 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
useDocUnwarping |
boolean | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 use_doc_unwarping 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
useLayoutDetection |
boolean | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 use_layout_detection 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
useChartRecognition |
boolean | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 use_chart_recognition 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
layoutThreshold |
number | object | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 layout_threshold 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
layoutNms |
boolean | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 layout_nms 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
layoutUnclipRatio |
number | array | object | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 layout_unclip_ratio 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
layoutMergeBboxesMode |
string | object | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 layout_merge_bboxes_mode 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
promptLabel |
string | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 prompt_label 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
formatBlockContent |
boolean | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 format_block_content 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
repetitionPenalty |
number | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 repetition_penalty 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
temperature |
number | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 temperature 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
topP |
number | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 top_p 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
minPixels |
number | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 min_pixels 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
maxPixels |
number | null |
请参阅PaddleOCR-VL对象中 predict 方法的 max_pixels 参数相关说明。 |
否 |
prettifyMarkdown |
boolean |
是否输出美化后的 Markdown 文本。默认为 true。 |
否 |
showFormulaNumber |
boolean |
输出的 Markdown 文本中是否包含公式编号。默认为 false。 |
否 |
visualize |
boolean | null |
是否返回可视化结果图以及处理过程中的中间图像等。
例如,在配置文件中添加如下字段: visualize参数可以覆盖默认行为。如果请求体和配置文件中均未设置(或请求体传入null、配置文件中未设置),则默认返回图像。
|
否 |
- 请求处理成功时,响应体的
result具有如下属性:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
layoutParsingResults |
array |
版面解析结果。数组长度为1(对于图像输入)或实际处理的文档页数(对于PDF输入)。对于PDF输入,数组中的每个元素依次表示PDF文件中实际处理的每一页的结果。 |
dataInfo |
object |
输入数据信息。 |
layoutParsingResults中的每个元素为一个object,具有如下属性:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
prunedResult |
object |
对象的 predict 方法生成结果的 JSON 表示中 res 字段的简化版本,其中去除了 input_path 和 page_index 字段。 |
markdown |
object |
Markdown结果。 |
outputImages |
object | null |
参见预测结果的 img 属性说明。图像为JPEG格式,使用Base64编码。 |
inputImage |
string | null |
输入图像。图像为JPEG格式,使用Base64编码。 |
markdown为一个object,具有如下属性:
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
text |
string |
Markdown文本。 |
images |
object |
Markdown图片相对路径和Base64编码图像的键值对。 |
isStart |
boolean |
当前页面第一个元素是否为段开始。 |
isEnd |
boolean |
当前页面最后一个元素是否为段结束。 |
多语言调用服务示例
Python
import base64
import requests
import pathlib
API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing" # 服务URL
image_path = "./demo.jpg"
# 对本地图像进行Base64编码
with open(image_path, "rb") as file:
image_bytes = file.read()
image_data = base64.b64encode(image_bytes).decode("ascii")
payload = {
"file": image_data, # Base64编码的文件内容或者文件URL
"fileType": 1, # 文件类型,1表示图像文件
}
# 调用API
response = requests.post(API_URL, json=payload)
# 处理接口返回数据
assert response.status_code == 200
result = response.json()["result"]
for i, res in enumerate(result["layoutParsingResults"]):
print(res["prunedResult"])
md_dir = pathlib.Path(f"markdown_{i}")
md_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
(md_dir / "doc.md").write_text(res["markdown"]["text"])
for img_path, img in res["markdown"]["images"].items():
img_path = md_dir / img_path
img_path.parent.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
img_path.write_bytes(base64.b64decode(img))
print(f"Markdown document saved at {md_dir / 'doc.md'}")
for img_name, img in res["outputImages"].items():
img_path = f"{img_name}_{i}.jpg"
pathlib.Path(img_path).parent.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
with open(img_path, "wb") as f:
f.write(base64.b64decode(img))
print(f"Output image saved at {img_path}")
C++
#include <iostream>
#include <filesystem>
#include <fstream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include "cpp-httplib/httplib.h" // https://github.com/Huiyicc/cpp-httplib
#include "nlohmann/json.hpp" // https://github.com/nlohmann/json
#include "base64.hpp" // https://github.com/tobiaslocker/base64
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
int main() {
httplib::Client client("localhost", 8080);
const std::string filePath = "./demo.jpg";
std::ifstream file(filePath, std::ios::binary | std::ios::ate);
if (!file) {
std::cerr << "Error opening file: " << filePath << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::streamsize size = file.tellg();
file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg);
std::vector buffer(size);
if (!file.read(buffer.data(), size)) {
std::cerr << "Error reading file." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
std::string bufferStr(buffer.data(), static_cast(size));
std::string encodedFile = base64::to_base64(bufferStr);
nlohmann::json jsonObj;
jsonObj["file"] = encodedFile;
jsonObj["fileType"] = 1;
auto response = client.Post("/layout-parsing", jsonObj.dump(), "application/json");
if (response && response->status == 200) {
nlohmann::json jsonResponse = nlohmann::json::parse(response->body);
auto result = jsonResponse["result"];
if (!result.is_object() || !result.contains("layoutParsingResults")) {
std::cerr << "Unexpected response format." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
const auto& results = result["layoutParsingResults"];
for (size_t i = 0; i < results.size(); ++i) {
const auto& res = results[i];
if (res.contains("prunedResult")) {
std::cout << "Layout result [" << i << "]: " << res["prunedResult"].dump() << std::endl;
}
if (res.contains("outputImages") && res["outputImages"].is_object()) {
for (auto& [imgName, imgBase64] : res["outputImages"].items()) {
std::string outputPath = imgName + "_" + std::to_string(i) + ".jpg";
fs::path pathObj(outputPath);
fs::path parentDir = pathObj.parent_path();
if (!parentDir.empty() && !fs::exists(parentDir)) {
fs::create_directories(parentDir);
}
std::string decodedImage = base64::from_base64(imgBase64.get());
std::ofstream outFile(outputPath, std::ios::binary);
if (outFile.is_open()) {
outFile.write(decodedImage.c_str(), decodedImage.size());
outFile.close();
std::cout << "Saved image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
} else {
std::cerr << "Failed to save image: " << outputPath << std::endl;
}
}
}
}
} else {
std::cerr << "Request failed." << std::endl;
if (response) {
std::cerr << "HTTP status: " << response->status << std::endl;
std::cerr << "Response body: " << response->body << std::endl;
}
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
Java
import okhttp3.*;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonNode;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Base64;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.nio.file.Files;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
String imagePath = "./demo.jpg";
File file = new File(imagePath);
byte[] fileContent = java.nio.file.Files.readAllBytes(file.toPath());
String base64Image = Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(fileContent);
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
ObjectNode payload = objectMapper.createObjectNode();
payload.put("file", base64Image);
payload.put("fileType", 1);
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
MediaType JSON = MediaType.get("application/json; charset=utf-8");
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(JSON, payload.toString());
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url(API_URL)
.post(body)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
String responseBody = response.body().string();
JsonNode root = objectMapper.readTree(responseBody);
JsonNode result = root.get("result");
JsonNode layoutParsingResults = result.get("layoutParsingResults");
for (int i = 0; i < layoutParsingResults.size(); i++) {
JsonNode item = layoutParsingResults.get(i);
int finalI = i;
JsonNode prunedResult = item.get("prunedResult");
System.out.println("Pruned Result [" + i + "]: " + prunedResult.toString());
JsonNode outputImages = item.get("outputImages");
outputImages.fieldNames().forEachRemaining(imgName -> {
try {
String imgBase64 = outputImages.get(imgName).asText();
byte[] imgBytes = Base64.getDecoder().decode(imgBase64);
String imgPath = imgName + "_" + finalI + ".jpg";
File outputFile = new File(imgPath);
File parentDir = outputFile.getParentFile();
if (parentDir != null && !parentDir.exists()) {
parentDir.mkdirs();
System.out.println("Created directory: " + parentDir.getAbsolutePath());
}
try (FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(outputFile)) {
fos.write(imgBytes);
System.out.println("Saved image: " + imgPath);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Failed to save image: " + e.getMessage());
}
});
}
} else {
System.err.println("Request failed with HTTP code: " + response.code());
}
}
}
}
Go
package main
import (
"bytes"
"encoding/base64"
"encoding/json"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"net/http"
"os"
"path/filepath"
)
func main() {
API_URL := "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing"
filePath := "./demo.jpg"
fileBytes, err := ioutil.ReadFile(filePath)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading file: %v\n", err)
return
}
fileData := base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(fileBytes)
payload := map[string]interface{}{
"file": fileData,
"fileType": 1,
}
payloadBytes, err := json.Marshal(payload)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error marshaling payload: %v\n", err)
return
}
client := &http.Client{}
req, err := http.NewRequest("POST", API_URL, bytes.NewBuffer(payloadBytes))
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating request: %v\n", err)
return
}
req.Header.Set("Content-Type", "application/json")
res, err := client.Do(req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error sending request: %v\n", err)
return
}
defer res.Body.Close()
if res.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
fmt.Printf("Unexpected status code: %d\n", res.StatusCode)
return
}
body, err := ioutil.ReadAll(res.Body)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error reading response: %v\n", err)
return
}
type Markdown struct {
Text string `json:"text"`
Images map[string]string `json:"images"`
}
type LayoutResult struct {
PrunedResult map[string]interface{} `json:"prunedResult"`
Markdown Markdown `json:"markdown"`
OutputImages map[string]string `json:"outputImages"`
InputImage *string `json:"inputImage"`
}
type Response struct {
Result struct {
LayoutParsingResults []LayoutResult `json:"layoutParsingResults"`
DataInfo interface{} `json:"dataInfo"`
} `json:"result"`
}
var respData Response
if err := json.Unmarshal(body, &respData); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error parsing response: %v\n", err)
return
}
for i, res := range respData.Result.LayoutParsingResults {
fmt.Printf("Result %d - prunedResult: %+v\n", i, res.PrunedResult)
mdDir := fmt.Sprintf("markdown_%d", i)
os.MkdirAll(mdDir, 0755)
mdFile := filepath.Join(mdDir, "doc.md")
if err := os.WriteFile(mdFile, []byte(res.Markdown.Text), 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error writing markdown file: %v\n", err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Markdown document saved at %s\n", mdFile)
}
for path, imgBase64 := range res.Markdown.Images {
fullPath := filepath.Join(mdDir, path)
if err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(fullPath), 0755); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating directory for markdown image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
imgBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(imgBase64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding markdown image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
if err := os.WriteFile(fullPath, imgBytes, 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error saving markdown image: %v\n", err)
}
}
for name, imgBase64 := range res.OutputImages {
imgBytes, err := base64.StdEncoding.DecodeString(imgBase64)
if err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error decoding output image %s: %v\n", name, err)
continue
}
filename := fmt.Sprintf("%s_%d.jpg", name, i)
if err := os.MkdirAll(filepath.Dir(filename), 0755); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error creating directory for output image: %v\n", err)
continue
}
if err := os.WriteFile(filename, imgBytes, 0644); err != nil {
fmt.Printf("Error saving output image %s: %v\n", filename, err)
} else {
fmt.Printf("Output image saved at %s\n", filename)
}
}
}
}
C#
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Newtonsoft.Json.Linq;
class Program
{
static readonly string API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
static readonly string inputFilePath = "./demo.jpg";
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
byte[] fileBytes = File.ReadAllBytes(inputFilePath);
string fileData = Convert.ToBase64String(fileBytes);
var payload = new JObject
{
{ "file", fileData },
{ "fileType", 1 }
};
var content = new StringContent(payload.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
HttpResponseMessage response = await httpClient.PostAsync(API_URL, content);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
string responseBody = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
JObject jsonResponse = JObject.Parse(responseBody);
JArray layoutParsingResults = (JArray)jsonResponse["result"]["layoutParsingResults"];
for (int i = 0; i < layoutParsingResults.Count; i++)
{
var res = layoutParsingResults[i];
Console.WriteLine($"[{i}] prunedResult:\n{res["prunedResult"]}");
JObject outputImages = res["outputImages"] as JObject;
if (outputImages != null)
{
foreach (var img in outputImages)
{
string imgName = img.Key;
string base64Img = img.Value?.ToString();
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(base64Img))
{
string imgPath = $"{imgName}_{i}.jpg";
byte[] imageBytes = Convert.FromBase64String(base64Img);
string directory = Path.GetDirectoryName(imgPath);
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(directory) && !Directory.Exists(directory))
{
Directory.CreateDirectory(directory);
Console.WriteLine($"Created directory: {directory}");
}
File.WriteAllBytes(imgPath, imageBytes);
Console.WriteLine($"Output image saved at {imgPath}");
}
}
}
}
}
}
Node.js
const axios = require('axios');
const fs = require('fs');
const path = require('path');
const API_URL = 'http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing';
const imagePath = './demo.jpg';
const fileType = 1;
function encodeImageToBase64(filePath) {
const bitmap = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
return Buffer.from(bitmap).toString('base64');
}
const payload = {
file: encodeImageToBase64(imagePath),
fileType: fileType
};
axios.post(API_URL, payload)
.then(response => {
const results = response.data.result.layoutParsingResults;
results.forEach((res, index) => {
console.log(`\n[${index}] prunedResult:`);
console.log(res.prunedResult);
const outputImages = res.outputImages;
if (outputImages) {
Object.entries(outputImages).forEach(([imgName, base64Img]) => {
const imgPath = `${imgName}_${index}.jpg`;
const directory = path.dirname(imgPath);
if (!fs.existsSync(directory)) {
fs.mkdirSync(directory, { recursive: true });
console.log(`Created directory: ${directory}`);
}
fs.writeFileSync(imgPath, Buffer.from(base64Img, 'base64'));
console.log(`Output image saved at ${imgPath}`);
});
} else {
console.log(`[${index}] No outputImages.`);
}
});
})
.catch(error => {
console.error('Error during API request:', error.message || error);
});
PHP
<?php
$API_URL = "http://localhost:8080/layout-parsing";
$image_path = "./demo.jpg";
$image_data = base64_encode(file_get_contents($image_path));
$payload = array("file" => $image_data, "fileType" => 1);
$ch = curl_init($API_URL);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POST, true);
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_POSTFIELDS, json_encode($payload));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_HTTPHEADER, array('Content-Type: application/json'));
curl_setopt($ch, CURLOPT_RETURNTRANSFER, true);
$response = curl_exec($ch);
curl_close($ch);
$result = json_decode($response, true)["result"]["layoutParsingResults"];
foreach ($result as $i => $item) {
echo "[$i] prunedResult:\n";
print_r($item["prunedResult"]);
if (!empty($item["outputImages"])) {
foreach ($item["outputImages"] as $img_name => $img_base64) {
$output_image_path = "{$img_name}_{$i}.jpg";
$directory = dirname($output_image_path);
if (!is_dir($directory)) {
mkdir($directory, 0777, true);
echo "Created directory: $directory\n";
}
file_put_contents($output_image_path, base64_decode($img_base64));
echo "Output image saved at $output_image_path\n";
}
} else {
echo "No outputImages found for item $i\n";
}
}
?>
4.4 产线配置调整说明
若您无需调整产线配置,可忽略此小节。
调整服务化部署的 PaddleOCR-VL 配置只需以下三步:
- 获取配置文件
- 修改配置文件
- 应用配置文件
4.4.1 获取配置文件
若您使用 Docker Compose 部署:
根据使用的后端,下载对应的产线配置文件:
- vLLM:pipeline_config_vllm.yaml
- FastDeploy:pipeline_config_fastdeploy.yaml
若您手动安装依赖部署:
执行以下命令生成产线配置文件:
paddlex --get_pipeline_config PaddleOCR-VL
4.4.2 修改配置文件
使用加速框架提升 VLM 推理性能
如需使用 vLLM 等加速框架提升 VLM 推理性能(第 2 节详细介绍如何启动 VLM 推理服务),可在产线配置文件中修改 VLRecognition.genai_config.backend 和 VLRecognition.genai_config.server_url 字段,例如:
VLRecognition:
...
genai_config:
backend: vllm-server
server_url: http://127.0.0.1:8118/v1
Docker Compose 方案默认已使用加速框架。
启用文档图像预处理功能
默认配置启动的服务不支持文档预处理功能。若客户端调用该功能,将返回错误信息。如需启用文档预处理,请在产线配置文件中将 use_doc_preprocessor 设置为 True,并使用修改后的配置文件启动服务。
禁用结果可视化功能
服务默认返回可视化结果,这会引入额外开销。如需禁用该功能,可在产线配置文件中添加如下配置(Serving 为顶层字段):
Serving:
visualize: False
此外,也可在请求体中设置 visualize 字段为 false,以针对单次请求禁用可视化。
配置返回图像 URL
对于可视化结果图及 Markdown 中包含的图像,服务默认以 Base64 编码返回。如需以 URL 形式返回图像,可在产线配置文件中添加如下配置(Serving 为顶层字段):
Serving:
extra:
file_storage:
type: bos
endpoint: https://bj.bcebos.com
bucket_name: some-bucket
ak: xxx
sk: xxx
key_prefix: deploy
return_img_urls: True
目前支持将生成的图像存储至百度智能云对象存储(BOS)并返回 URL。相关参数说明如下:
endpoint:访问域名,必须配置。ak:百度智能云 AK,必须配置。sk:百度智能云 SK,必须配置。bucket_name:存储空间名称,必须配置。key_prefix:Object key 的统一前缀。connection_timeout_in_mills:请求超时时间(单位:毫秒)。
有关 AK/SK 获取等更多信息,请参考 百度智能云官方文档。
修改 PDF 解析页数限制
出于性能考虑,服务默认仅处理接收到的 PDF 文件的前 10 页。如需调整页数限制,可在产线配置文件中添加如下配置(Serving 为顶层字段):
Serving:
extra:
max_num_input_imgs: <新的页数限制,例如 100>
将 max_num_input_imgs 设置为 null 可解除页数限制。
4.4.3 应用配置文件
若您使用 Docker Compose 部署:
设置 Compose 文件中的 services.paddleocr-vl-api.volumes 字段,将产线配置文件挂载到 /home/paddleocr 目录。例如:
services:
paddleocr-vl-api:
...
volumes:
- pipeline_config_vllm.yaml:/home/paddleocr/pipeline_config.yaml
...
在生产环境中,您也可以自行构建镜像,将配置文件打包到镜像中。
若您手动安装依赖部署:
在启动服务时,将 --pipeline 参数指定为自定义配置文件路径。
5. 模型微调
若您发现 PaddleOCR-VL 在特定业务场景中的精度表现未达预期,我们推荐使用 ERNIEKit 套件 对 PaddleOCR-VL-0.9B 模型进行有监督微调(SFT)。具体操作步骤可参考 ERNIEKit 官方文档。
目前暂不支持对版面检测排序模型进行微调。