diff --git a/docs-website/sidebars.js b/docs-website/sidebars.js
index f95a1ac58c..986066ee14 100644
--- a/docs-website/sidebars.js
+++ b/docs-website/sidebars.js
@@ -914,6 +914,7 @@ module.exports = {
},
"docs/api/tutorials/owners",
"docs/api/tutorials/structured-properties",
+ "docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions",
"docs/api/tutorials/tags",
"docs/api/tutorials/terms",
{
diff --git a/docs/api/tutorials/assertions.md b/docs/api/tutorials/assertions.md
index 915c37630d..db28f13718 100644
--- a/docs/api/tutorials/assertions.md
+++ b/docs/api/tutorials/assertions.md
@@ -29,11 +29,11 @@ The actor making API calls must have the `Edit Assertions` and `Edit Monitors` p
You can create new dataset Assertions to DataHub using the following APIs.
+### Freshness Assertion
+
-### Freshness Assertion
-
To create a new freshness assertion, use the `upsertDatasetFreshnessAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
```graphql
@@ -71,10 +71,108 @@ This API will return a unique identifier (URN) for the new assertion if you were
}
```
+
+
+
+```python
+from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
+from datahub.metadata.urns import DatasetUrn
+
+# Initialize the client
+client = DataHubClient(server="", token="")
+
+# Create smart freshness assertion (AI-powered anomaly detection)
+dataset_urn = DatasetUrn.from_string("urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:snowflake,database.schema.table,PROD)")
+
+smart_freshness_assertion = client.assertions.sync_smart_freshness_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Smart Freshness Anomaly Monitor",
+ # Detection mechanism - information_schema is recommended
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ # Smart sensitivity setting
+ sensitivity="medium", # options: "low", "medium", "high"
+ # Tags for grouping
+ tags=["automated", "freshness", "data_quality"],
+ # Enable the assertion
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created smart freshness assertion: {smart_freshness_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Create traditional freshness assertion (fixed interval)
+freshness_assertion = client.assertions.sync_freshness_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Fixed Interval Freshness Check",
+ # Fixed interval check - table should be updated within lookback window
+ freshness_schedule_check_type="fixed_interval",
+ # Lookback window - table should be updated within 8 hours
+ lookback_window={"unit": "HOUR", "multiple": 8},
+ # Detection mechanism
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ # Evaluation schedule - how often to check
+ schedule="0 */2 * * *", # Check every 2 hours
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "freshness", "fixed_interval"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created freshness assertion: {freshness_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Create since-last-check freshness assertion
+since_last_check_assertion = client.assertions.sync_freshness_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Since Last Check Freshness",
+ # Since last check - table should be updated since the last evaluation
+ freshness_schedule_check_type="since_the_last_check",
+ # Detection mechanism with last modified column
+ detection_mechanism={
+ "type": "last_modified_column",
+ "column_name": "updated_at",
+ "additional_filter": "status = 'active'"
+ },
+ # Evaluation schedule - how often to check
+ schedule="0 */6 * * *", # Check every 6 hours
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "freshness", "since_last_check"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created since last check assertion: {since_last_check_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Create freshness assertion with high watermark column
+watermark_freshness_assertion = client.assertions.sync_freshness_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="High Watermark Freshness Check",
+ # Fixed interval check with specific lookback window
+ freshness_schedule_check_type="fixed_interval",
+ # Lookback window - check for updates in the last 24 hours
+ lookback_window={"unit": "DAY", "multiple": 1},
+ # Detection mechanism using high watermark column (e.g., auto-incrementing ID)
+ detection_mechanism={
+ "type": "high_watermark_column",
+ "column_name": "id",
+ "additional_filter": "status != 'deleted'"
+ },
+ # Evaluation schedule
+ schedule="0 8 * * *", # Check daily at 8 AM
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "freshness", "high_watermark"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created watermark freshness assertion: {watermark_freshness_assertion.urn}")
+```
+
+
+
+
For more details, see the [Freshness Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/freshness-assertions.md) guide.
### Volume Assertions
+
+
+
To create a new volume assertion, use the `upsertDatasetVolumeAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
```graphql
@@ -116,10 +214,94 @@ This API will return a unique identifier (URN) for the new assertion if you were
}
```
+
+
+
+
+
+```python
+from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
+from datahub.metadata.urns import DatasetUrn
+
+# Initialize the client
+client = DataHubClient(server="", token="")
+
+# Create smart volume assertion (AI-powered anomaly detection)
+dataset_urn = DatasetUrn.from_string("urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:snowflake,database.schema.table,PROD)")
+
+smart_volume_assertion = client.assertions.sync_smart_volume_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Smart Volume Check",
+ # Detection mechanism options
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ # Smart sensitivity setting
+ sensitivity="medium", # options: "low", "medium", "high"
+ # Tags for grouping
+ tags=["automated", "volume", "data_quality"],
+ # Schedule (optional - defaults to hourly)
+ schedule="0 */6 * * *", # Every 6 hours
+ # Enable the assertion
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created smart volume assertion: {smart_volume_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Create traditional volume assertion (fixed threshold range)
+volume_assertion = client.assertions.sync_volume_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Row Count Range Check",
+ criteria_condition="ROW_COUNT_IS_WITHIN_A_RANGE",
+ criteria_parameters=(1000, 10000), # Between 1000 and 10000 rows
+ # Detection mechanism
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ # Evaluation schedule
+ schedule="0 */4 * * *", # Every 4 hours
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "volume", "threshold_check"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created volume assertion: {volume_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Example with single threshold
+min_volume_assertion = client.assertions.sync_volume_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Minimum Row Count Check",
+ criteria_condition="ROW_COUNT_IS_GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUAL_TO",
+ criteria_parameters=500, # At least 500 rows
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ schedule="0 */2 * * *", # Every 2 hours
+ tags=["automated", "volume", "minimum_check"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created minimum volume assertion: {min_volume_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Example with growth-based assertion
+growth_volume_assertion = client.assertions.sync_volume_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Daily Growth Check",
+ criteria_condition="ROW_COUNT_GROWS_BY_AT_MOST_ABSOLUTE",
+ criteria_parameters=1000, # Grows by at most 1000 rows between checks
+ detection_mechanism="information_schema",
+ schedule="0 6 * * *", # Daily at 6 AM
+ tags=["automated", "volume", "growth_check"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created growth volume assertion: {growth_volume_assertion.urn}")
+```
+
+
+
+
For more details, see the [Volume Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/volume-assertions.md) guide.
### Column Assertions
+
+
+
To create a new column assertion, use the `upsertDatasetFieldAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
```graphql
@@ -165,11 +347,64 @@ This API will return a unique identifier (URN) for the new assertion if you were
}
```
+
+
+
+```python
+from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
+from datahub.metadata.urns import DatasetUrn
+
+# Initialize the client
+client = DataHubClient(server="", token="")
+
+# Create smart column metric assertion (AI-powered anomaly detection)
+dataset_urn = DatasetUrn.from_string("urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:snowflake,database.schema.table,PROD)")
+
+smart_column_assertion = client.assertions.sync_smart_column_metric_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ column_name="user_id",
+ metric_type="null_count",
+ display_name="Smart Null Count Check - user_id",
+ # Detection mechanism for column metrics
+ detection_mechanism="all_rows_query_datahub_dataset_profile",
+ # Smart sensitivity setting
+ sensitivity="medium", # options: "low", "medium", "high"
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "column_quality", "null_checks"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created smart column assertion: {smart_column_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Create regular column metric assertion (fixed threshold)
+column_assertion = client.assertions.sync_column_metric_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ column_name="price",
+ metric_type="min",
+ operator="greater_than_or_equal_to",
+ criteria_parameters=0,
+ display_name="Price Minimum Check",
+ # Evaluation schedule
+ schedule="0 */4 * * *", # Every 4 hours
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "column_quality", "price_validation"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created column assertion: {column_assertion.urn}")
+```
+
+
+
+
For more details, see the [Column Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/column-assertions.md) guide.
### Custom SQL Assertions
-To create a new column assertion, use the `upsertDatasetSqlAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
+
+
+
+To create a new custom SQL assertion, use the `upsertDatasetSqlAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
```graphql
mutation upsertDatasetSqlAssertionMonitor {
@@ -207,10 +442,59 @@ This API will return a unique identifier (URN) for the new assertion if you were
}
```
+
+
+
+```python
+from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
+from datahub.metadata.urns import DatasetUrn
+
+# Initialize the client
+client = DataHubClient(server="", token="")
+
+# Create custom SQL assertion
+dataset_urn = DatasetUrn.from_string("urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:snowflake,database.schema.table,PROD)")
+
+sql_assertion = client.assertions.sync_sql_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Revenue Quality Check",
+ statement="SELECT SUM(revenue) FROM database.schema.table WHERE date >= CURRENT_DATE - INTERVAL '1 day'",
+ criteria_condition="IS_GREATER_THAN_OR_EQUAL_TO",
+ criteria_parameters=1000,
+ # Evaluation schedule
+ schedule="0 6 * * *", # Daily at 6 AM
+ # Tags
+ tags=["automated", "revenue", "data_quality"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created SQL assertion: {sql_assertion.urn}")
+
+# Example with range check
+range_sql_assertion = client.assertions.sync_sql_assertion(
+ dataset_urn=dataset_urn,
+ display_name="Daily Order Count Range Check",
+ statement="SELECT COUNT(*) FROM database.schema.orders WHERE DATE(created_at) = CURRENT_DATE",
+ criteria_condition="IS_WITHIN_A_RANGE",
+ criteria_parameters=(50, 500), # Between 50 and 500 orders per day
+ schedule="0 */6 * * *", # Every 6 hours
+ tags=["automated", "orders", "volume_check"],
+ enabled=True
+)
+
+print(f"Created range SQL assertion: {range_sql_assertion.urn}")
+```
+
+
+
+
For more details, see the [Custom SQL Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/custom-sql-assertions.md) guide.
### Schema Assertions
+
+
+
To create a new schema assertion, use the `upsertDatasetSchemaAssertionMonitor` GraphQL Mutation.
```graphql
@@ -248,11 +532,11 @@ This API will return a unique identifier (URN) for the new assertion if you were
}
```
-For more details, see the [Schema Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/schema-assertions.md) guide.
-
+For more details, see the [Schema Assertions](/docs/managed-datahub/observe/schema-assertions.md) guide.
+
## Run Assertions
You can use the following APIs to trigger the assertions you've created to run on-demand. This is
@@ -1163,30 +1447,6 @@ urn:li:assertion:
3. Generate the [**AssertionRunEvent**](/docs/generated/metamodel/entities/assertion.md#assertionrunevent-timeseries) timeseries aspect using the Python SDK. This aspect should contain the result of the assertion
run at a given timestamp and will be shown on the results graph in DataHub's UI.
-## Create Subscription
+## Create and Remove Subscriptions
-You can create subscriptions to receive notifications when assertions change state (pass, fail, or error) or when other entity changes occur. Subscriptions can be created at the dataset level (affecting all assertions on the dataset) or at the assertion level (affecting only specific assertions).
-
-
-
-
-```python
-{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/create_subscription.py show_path_as_comment }}
-```
-
-
-
-
-## Remove Subscription
-
-You can remove existing subscriptions to stop receiving notifications. The unsubscribe method supports selective removal of specific change types or complete removal of subscriptions.
-
-
-
-
-```python
-{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/remove_subscription.py show_path_as_comment }}
-```
-
-
-
+Reference the [Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md) for more information on how to create and remove subscriptions on Datasets or Assertions.
diff --git a/docs/api/tutorials/sdk/bulk-assertions-sdk.md b/docs/api/tutorials/sdk/bulk-assertions-sdk.md
index c7fcddcd2c..a23e631121 100644
--- a/docs/api/tutorials/sdk/bulk-assertions-sdk.md
+++ b/docs/api/tutorials/sdk/bulk-assertions-sdk.md
@@ -5,7 +5,7 @@ import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
-This guide specifically covers how to use the DataHub Cloud Python SDK for **bulk creating smart assertions**, including:
+This guide specifically covers how to use the [DataHub Cloud Python SDK](https://pypi.org/project/acryl-datahub-cloud/) for **bulk creating smart assertions**, including:
- Smart Freshness Assertions
- Smart Volume Assertions
@@ -33,7 +33,7 @@ The actor making API calls must have the `Edit Assertions` and `Edit Monitors` p
:::note
Before creating assertions, you need to ensure the target datasets are already present in your DataHub instance.
-If you attempt to create assertions for entities that do not exist, your operation will fail.
+If you attempt to create assertions for entities that do not exist, GMS will continuously report errors to the logs.
:::
### Goal Of This Guide
@@ -73,6 +73,12 @@ from datahub.sdk import DataHubClient
client = DataHubClient.from_env()
```
+## Important Considerations for Parallel Processing
+
+- Always run bulk assertion creation for a given dataset in a single thread to avoid race conditions.
+- Always call subscription APIs for a given dataset in a single thread to avoid race conditions.
+ - If you are subscribing to assertions directly, make sure to also run the script on a single thread per dataset.
+
## Step 1: Discover Tables
### Option A: Get Specific Tables
@@ -339,7 +345,15 @@ def should_apply_rule(column_name, column_type, rule_config):
create_column_assertions(datasets, dataset_columns, client, assertion_registry)
```
-## Step 5: Store Assertion URNs
+## Step 5: Create Subscription
+
+Reference the [Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md) for more information on how to create subscriptions on Datasets or Assertions.
+
+:::note
+When creating subscriptions in bulk, you must perform the operation in a single thread to avoid race conditions. Additionally, we recommend creating subscriptions at the dataset level rather than for individual assertions, as this makes ongoing management much easier.
+:::
+
+## Step 6: Store Assertion URNs
### Save to File
@@ -389,7 +403,7 @@ def load_assertion_registry(filename):
# assertion_registry = load_assertion_registry("assertion_registry_20240101_120000.json")
```
-## Step 6: Update Existing Assertions
+## Step 7: Update Existing Assertions
```python
def update_existing_assertions(registry, client):
diff --git a/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md b/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..8f6c4f7379
--- /dev/null
+++ b/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md
@@ -0,0 +1,119 @@
+import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
+import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
+
+# Subscriptions
+
+
+
+## Why Would You Use Subscriptions on Datasets?
+
+Subscriptions are a way to receive notifications when entity changes occur (e.g. deprecations, schema changes, ownership changes, etc.) or when assertions change state (pass, fail, or error). Subscriptions can be created at the dataset level (affecting any changes on the dataset, as well as all assertions on the dataset) or at the assertion level (affecting only specific assertions).
+
+### Goal Of This Guide
+
+This guide specifically covers how to use the [DataHub Cloud Python SDK](https://pypi.org/project/acryl-datahub-cloud/) for managing Subscriptions:
+
+- Create: create a subscription to a dataset or assertion.
+- Remove: remove a subscription.
+
+# Prerequisites
+
+- DataHub Cloud Python SDK installed (`pip install acryl-datahub-cloud`)
+- The actor making API calls must have the `Manage User Subscriptions` privilege for the datasets at hand.
+- If subscribing to a group, the actor should also be a member of the group.
+
+:::note
+Before creating subscriptions, you need to ensure the target datasets and groups are already present in your DataHub instance.
+If you attempt to create subscriptions for entities that do not exist, GMS will continuously report errors to the logs.
+:::
+
+## Create Subscription
+
+You can create subscriptions to receive notifications when assertions change state (pass, fail, or error) or when other entity changes occur. Subscriptions can be created at the dataset level (affecting any changes on the dataset, as well as all assertions on the dataset) or at the assertion level (affecting only specific assertions).
+
+
+
+
+```python
+{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/create_subscription.py show_path_as_comment }}
+```
+
+
+
+
+## Remove Subscription
+
+You can remove existing subscriptions to stop receiving notifications. The unsubscribe method supports selective removal of specific change types or complete removal of subscriptions.
+
+
+
+
+```python
+{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/remove_subscription.py show_path_as_comment }}
+```
+
+
+
+
+# Available Change Types
+
+The following change types are available for subscriptions:
+
+#### Schema Changes
+
+- `OPERATION_COLUMN_ADDED` - When a new column is added to a dataset
+- `OPERATION_COLUMN_REMOVED` - When a column is removed from a dataset
+- `OPERATION_COLUMN_MODIFIED` - When an existing column is modified
+
+#### Operational Metadata Changes
+
+- `OPERATION_ROWS_INSERTED` - When rows are inserted into a dataset
+- `OPERATION_ROWS_UPDATED` - When rows are updated in a dataset
+- `OPERATION_ROWS_REMOVED` - When rows are removed from a dataset
+
+#### Assertion Events
+
+- `ASSERTION_PASSED` - When an assertion run passes
+- `ASSERTION_FAILED` - When an assertion run fails
+- `ASSERTION_ERROR` - When an assertion run encounters an error
+
+#### Incident Status Changes
+
+- `INCIDENT_RAISED` - When a new incident is raised
+- `INCIDENT_RESOLVED` - When an incident is resolved
+
+#### Test Status Changes
+
+- `TEST_PASSED` - When a test passes
+- `TEST_FAILED` - When a test fails
+
+#### Deprecation Status Changes
+
+- `DEPRECATED` - When an entity is marked as deprecated
+- `UNDEPRECATED` - When an entity's deprecation status is removed
+
+#### Ingestion Status Changes
+
+- `INGESTION_SUCCEEDED` - When ingestion completes successfully
+- `INGESTION_FAILED` - When ingestion fails
+
+#### Documentation Changes
+
+- `DOCUMENTATION_CHANGE` - When documentation is modified
+
+#### Ownership Changes
+
+- `OWNER_ADDED` - When an owner is added to an entity
+- `OWNER_REMOVED` - When an owner is removed from an entity
+
+#### Glossary Term Changes
+
+- `GLOSSARY_TERM_ADDED` - When a glossary term is added to an entity
+- `GLOSSARY_TERM_REMOVED` - When a glossary term is removed from an entity
+- `GLOSSARY_TERM_PROPOSED` - When a glossary term is proposed for an entity
+
+#### Tag Changes
+
+- `TAG_ADDED` - When a tag is added to an entity
+- `TAG_REMOVED` - When a tag is removed from an entity
+- `TAG_PROPOSED` - When a tag is proposed for an entity
diff --git a/docs/managed-datahub/subscription-and-notification.md b/docs/managed-datahub/subscription-and-notification.md
index 711095c4fc..0d68547dd3 100644
--- a/docs/managed-datahub/subscription-and-notification.md
+++ b/docs/managed-datahub/subscription-and-notification.md
@@ -157,6 +157,10 @@ Then select individual assertions you'd like to subscribe to:
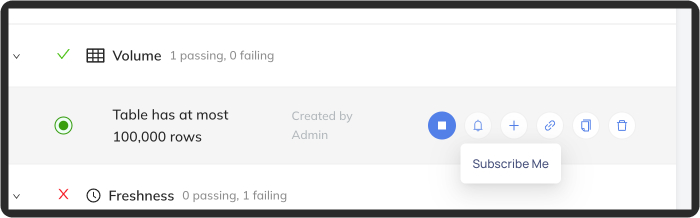 +## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ
+## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ
 +## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ
+## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ
 +## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ
+## Programatically Managing Subscriptions
+
+You can create and remove subscriptions programatically using the [GraphQL APIs](/docs/api/graphql/overview.md) or the [Python Subscriptions SDK](/docs/api/tutorials/subscriptions.md).
+
## FAQ