import Tabs from '@theme/Tabs';
import TabItem from '@theme/TabItem';
# Data Lineage
## Why Would You Use Lineage?
Data lineage is used to capture data dependencies within an organization. It allows you to track the inputs from which a data asset is derived, along with the data assets that depend on it downstream.
For more information about data lineage, refer to [About DataHub Lineage](/docs/generated/lineage/lineage-feature-guide.md).
### Goal Of This Guide
This guide will show you how to
- Add lineage between datasets.
- Add column-level lineage between datasets.
## Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you need to deploy DataHub Quickstart and ingest sample data.
For detailed steps, please refer to [Datahub Quickstart Guide](/docs/quickstart.md).
:::note
Before adding lineage, you need to ensure the targeted dataset is already present in your datahub.
If you attempt to manipulate entities that do not exist, your operation will fail.
In this guide, we will be using data from sample ingestion.
:::
## Add Lineage
```json
mutation updateLineage {
updateLineage(
input: {
edgesToAdd: [
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)"
}
]
edgesToRemove: []
}
)
}
```
Note that you can create a list of edges. For example, if you want to assign multiple upstream entities to a downstream entity, you can do the following.
```json
mutation updateLineage {
updateLineage(
input: {
edgesToAdd: [
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)"
}
{
downstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)"
upstreamUrn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_created,PROD)"
}
]
edgesToRemove: []
}
)
}
```
For more information about the `updateLineage` mutation, please refer to [updateLineage](https://datahubproject.io/docs/graphql/mutations/#updatelineage).
If you see the following response, the operation was successful:
```python
{
"data": {
"updateLineage": true
},
"extensions": {}
}
```
```shell
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ "query": "mutation updateLineage { updateLineage( input:{ edgesToAdd : { downstreamUrn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\", upstreamUrn : \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,logging_events,PROD)\"}, edgesToRemove :{downstreamUrn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\",upstreamUrn : \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:hive,fct_users_deleted,PROD)\" } })}", "variables":{}}'
```
Expected Response:
```json
{ "data": { "updateLineage": true }, "extensions": {} }
```
```python
{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/lineage_emitter_rest.py show_path_as_comment }}
```
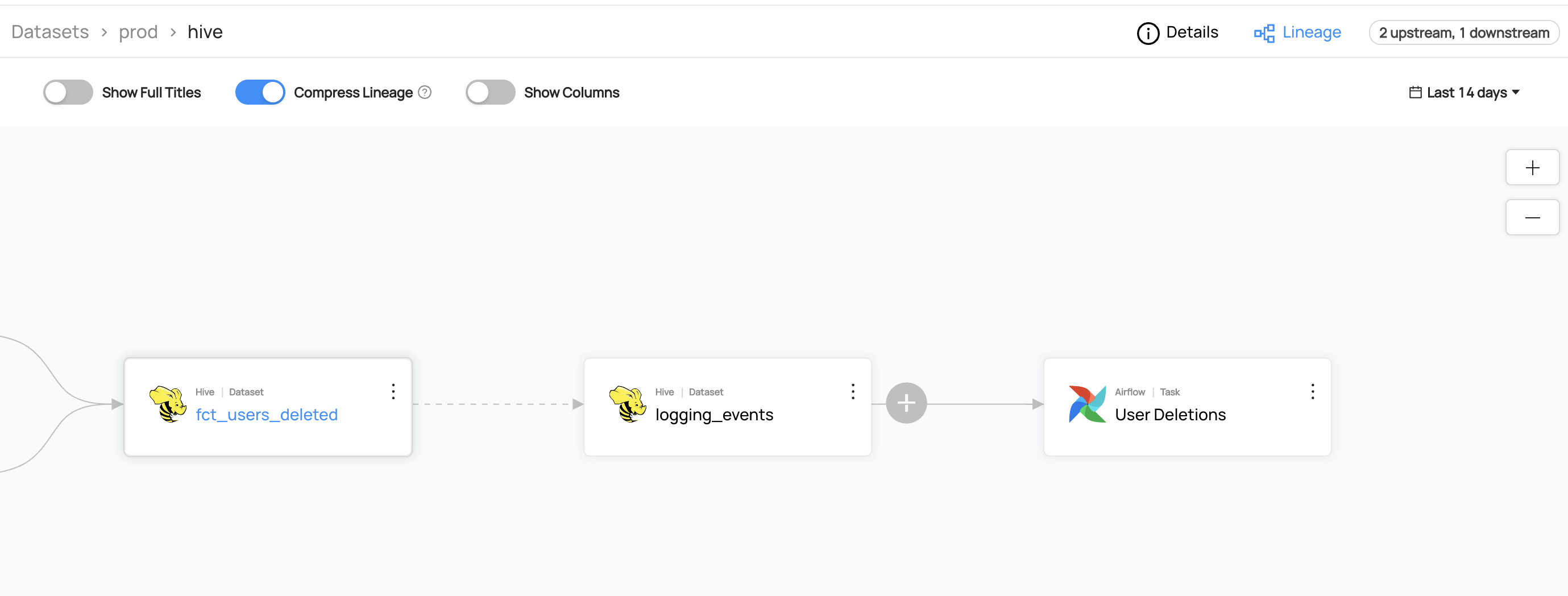
### Expected Outcomes of Adding Lineage
You can now see the lineage between `fct_users_deleted` and `logging_events`.
## Add Column-level Lineage
```python
{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/lineage_emitter_dataset_finegrained_sample.py show_path_as_comment }}
```
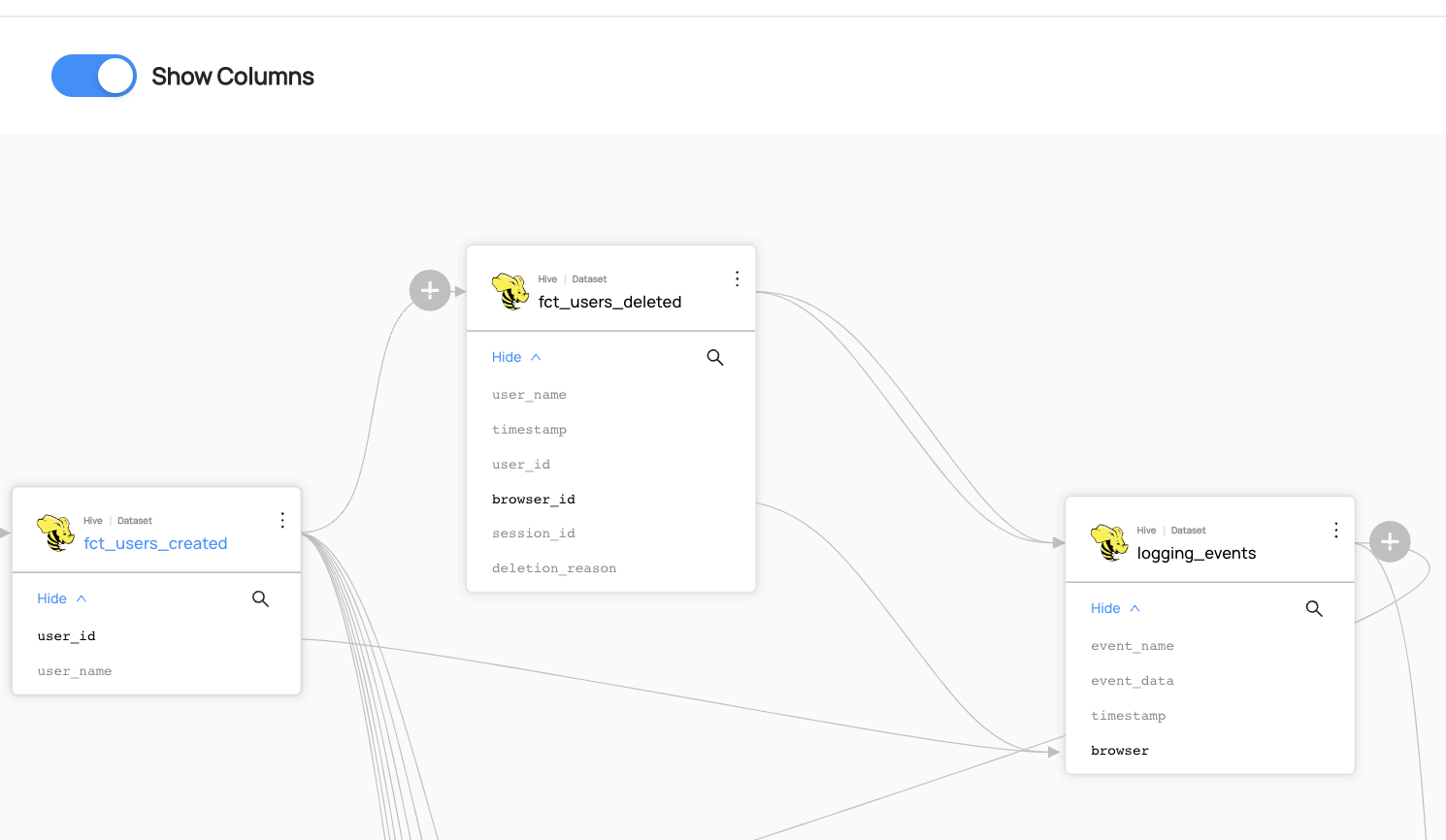
### Expected Outcome of Adding Column Level Lineage
You can now see the column-level lineage between datasets. Note that you have to enable `Show Columns` to be able to see the column-level lineage.
## Read Table Lineage
```graphql
query searchAcrossLineage {
searchAcrossLineage(
input: {
query: "*"
urn: "urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:dbt,long_tail_companions.adoption.human_profiles,PROD)"
start: 0
count: 10
direction: DOWNSTREAM
orFilters: [
{
and: [
{
condition: EQUAL
negated: false
field: "degree"
values: ["1", "2", "3+"]
}
]
}
]
}
) {
searchResults {
degree
entity {
urn
type
}
}
}
}
```
This example shows using lineage degrees as a filter, but additional search filters can be included here as well.
```shell
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ { "query": "query searchAcrossLineage { searchAcrossLineage( input: { query: \"*\" urn: \"urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:dbt,long_tail_companions.adoption.human_profiles,PROD)\" start: 0 count: 10 direction: DOWNSTREAM orFilters: [ { and: [ { condition: EQUAL negated: false field: \"degree\" values: [\"1\", \"2\", \"3+\"] } ] } ] } ) { searchResults { degree entity { urn type } } }}"
}}'
```
```python
{{ inline /metadata-ingestion/examples/library/read_lineage_rest.py show_path_as_comment }}
```
This will perform a multi-hop lineage search on the urn specified. For more information about the `searchAcrossLineage` mutation, please refer to [searchAcrossLineage](https://datahubproject.io/docs/graphql/queries/#searchacrosslineage).
## Read Column Lineage
```graphql
query searchAcrossLineage {
searchAcrossLineage(
input: {
query: "*"
urn: "urn:li:schemaField(urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:dbt,long_tail_companions.adoption.human_profiles,PROD),profile_id)"
start: 0
count: 10
direction: DOWNSTREAM
orFilters: [
{
and: [
{
condition: EQUAL
negated: false
field: "degree"
values: ["1", "2", "3+"]
}
]
}
]
}
) {
searchResults {
degree
entity {
urn
type
}
}
}
}
```
This example shows using lineage degrees as a filter, but additional search filters can be included here as well.
```shell
curl --location --request POST 'http://localhost:8080/api/graphql' \
--header 'Authorization: Bearer ' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' --data-raw '{ { "query": "query searchAcrossLineage { searchAcrossLineage( input: { query: \"*\" urn: \"urn:li:schemaField(urn:li:dataset:(urn:li:dataPlatform:dbt,long_tail_companions.adoption.human_profiles,PROD),profile_id)\" start: 0 count: 10 direction: DOWNSTREAM orFilters: [ { and: [ { condition: EQUAL negated: false field: \"degree\" values: [\"1\", \"2\", \"3+\"] } ] } ] } ) { searchResults { degree entity { urn type } } }}"
}}'
```
This will perform a multi-hop lineage search on the urn specified. You can see schemaField URNs are made up of two parts: first the table they are a column of, and second the path of the column. For more information about the `searchAcrossLineage` mutation, please refer to [searchAcrossLineage](https://datahubproject.io/docs/graphql/queries/#searchacrosslineage).


